Ev ve Ofis taşıma sektöründe lider olmak.Teknolojiyi klrd takip ederek bunu müşteri menuniyeti amacı için kullanmak.Sektörde marka olmak.
İstanbul evden eve nakliyat
Misyonumuz sayesinde edindiğimiz müşteri memnuniyeti ve güven ile müşterilerimizin bizi tavsiye etmelerini sağlamak.
Iris liveness detection by relative distance comparisons
.png) The focus of this paper is on presentation attack detection for the iris biometrics, which measures the pattern within the colored concentric circle of the subjects’ eyes, to authenticate an individual to a generic user verification system. Unlike previous deep learning methods that use single convolutional neural network architectures, this paper develops a framework built upon triplet convolutional networks that takes as input two real iris patches and a fake patch or two fake patches and a genuine patch. The smaller architecture provides a way to do early stopping based on the liveness of single patches rather than the whole image. The matching is performed by computing the distance with respect to a reference set of real and fake examples. The proposed approach allows for realtime processing using a smaller network and provides equal or better than state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets of photo-based and contact lens presentation attacks.
The focus of this paper is on presentation attack detection for the iris biometrics, which measures the pattern within the colored concentric circle of the subjects’ eyes, to authenticate an individual to a generic user verification system. Unlike previous deep learning methods that use single convolutional neural network architectures, this paper develops a framework built upon triplet convolutional networks that takes as input two real iris patches and a fake patch or two fake patches and a genuine patch. The smaller architecture provides a way to do early stopping based on the liveness of single patches rather than the whole image. The matching is performed by computing the distance with respect to a reference set of real and fake examples. The proposed approach allows for realtime processing using a smaller network and provides equal or better than state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets of photo-based and contact lens presentation attacks.
A Reference-Based Framework for Pose Invariant Face Recognition
 The similarity between a face image and a set of reference individuals defines the reference-based descriptor for a face image.
Recognition is performed using the reference-based descriptors of probe and gallery images. The dimensionality of the face descriptor generated
by the accompanying face recognition algorithm is reduced to the number of individuals in the reference set. The proposed framework is a
generalization of previous recognition methods that use indirect similarity and referencebased descriptors.
The similarity between a face image and a set of reference individuals defines the reference-based descriptor for a face image.
Recognition is performed using the reference-based descriptors of probe and gallery images. The dimensionality of the face descriptor generated
by the accompanying face recognition algorithm is reduced to the number of individuals in the reference set. The proposed framework is a
generalization of previous recognition methods that use indirect similarity and referencebased descriptors.
Reference Face Graph for Face Recognition
 Face recognition has been studied extensively; however, real-world face recognition still remains a
challenging task. We approach face recognition in the context of graph theory. We recognize an unknown face
using an external Reference Face Graph (RFG). A RFG is generated and recognition of a given face is achieved
by comparing it to the faces in the constructed RFG. The results show that the proposed approach outperforms
the state-of-the-art methods.
Face recognition has been studied extensively; however, real-world face recognition still remains a
challenging task. We approach face recognition in the context of graph theory. We recognize an unknown face
using an external Reference Face Graph (RFG). A RFG is generated and recognition of a given face is achieved
by comparing it to the faces in the constructed RFG. The results show that the proposed approach outperforms
the state-of-the-art methods.
Face biometrics in the wild
.png) Facial biometrics is a multidisciplinary field based on the methods and technologies of image analysis and machine learning, as applied to identifying people from facial information, and has progressed for over three decades in terms of theory, algorithms, and applications. While surveillance systems are in common practice and close-range facial recognition at entry points exist, the field has progressed beyond still image recognition in controlled imaging environments. In general, face recognition in the wild connotes recognition from still images and videos, unabated by age, pose, illumination, and expression (A-PIE) of individuals.
Facial biometrics is a multidisciplinary field based on the methods and technologies of image analysis and machine learning, as applied to identifying people from facial information, and has progressed for over three decades in terms of theory, algorithms, and applications. While surveillance systems are in common practice and close-range facial recognition at entry points exist, the field has progressed beyond still image recognition in controlled imaging environments. In general, face recognition in the wild connotes recognition from still images and videos, unabated by age, pose, illumination, and expression (A-PIE) of individuals.
Discrete Cosine Transform Locality-Sensitive Hashes for Face Retrieval
![Sample images from LFW [44],FERET [40], RaFD [42], BioID [43],FEI [41], and Multi-PIE [39]](../research_images/DiscreteCosineTransformLocality-SensitiveHashes14.png) Searching large databases using local binary patterns for face recognition has been problematic due to
the cost of the linear search, and the inadequate performance of existing indexing
methods. We present Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) hashing for creating index structures for
face descriptors. Hashes play the role of keywords: an index is created, and queried to find
the images most similar to the query image. It is shown here that DCT hashing has significantly
better retrieval accuracy and it is more efficient compared to other popular state-of-the-art
hash algorithms.
Searching large databases using local binary patterns for face recognition has been problematic due to
the cost of the linear search, and the inadequate performance of existing indexing
methods. We present Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) hashing for creating index structures for
face descriptors. Hashes play the role of keywords: an index is created, and queried to find
the images most similar to the query image. It is shown here that DCT hashing has significantly
better retrieval accuracy and it is more efficient compared to other popular state-of-the-art
hash algorithms.
Unconstrained Face Recognition in Surveillance Camera Networks
 Achieving good performance in surveillance videos with unconstrained faces is inherently difficult.
We aim at tackling this unconstrained face recognition problem and utilizing multiple cameras to improve the recognition
accuracy using a probabilistic approach.
The proposed method is tested on a public surveillance video dataset with a three-camera setup.
We compare our method to different benchmark classifiers with various feature descriptors.
The results demonstrate that by modeling the face in a dynamic manner the recognition performance
in a multi-camera network is improved and the recognition result is better than using any of the single cameras.
Achieving good performance in surveillance videos with unconstrained faces is inherently difficult.
We aim at tackling this unconstrained face recognition problem and utilizing multiple cameras to improve the recognition
accuracy using a probabilistic approach.
The proposed method is tested on a public surveillance video dataset with a three-camera setup.
We compare our method to different benchmark classifiers with various feature descriptors.
The results demonstrate that by modeling the face in a dynamic manner the recognition performance
in a multi-camera network is improved and the recognition result is better than using any of the single cameras.
Facial Emotion Recognition with Anisotropic Inhibited Gabor Energy Histograms
 State-of-the-art approaches have yet to deliver a feature representation
for facial emotion recognition that can be applied
to non-trivial unconstrained, continuous video data sets. Initially,
research advanced with the use of Gabor energy filters.
However, in recent work more attention has been given
to other features. Gabor energy filters lack generalization
needed in unconstrained situations. Additionally, they result
in an undesirably high feature vector dimensionality. Nontrivial
data sets have millions of samples; feature vectors must
be as low dimensional as possible. We propose a novel texture
feature based on Gabor energy filters that offers generalization
with a background texture suppression component and is
as compact as possible due to a maximal response representation
and local histograms. We improve performance on the
non-trivial Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2012 grandchallenge
data set.
State-of-the-art approaches have yet to deliver a feature representation
for facial emotion recognition that can be applied
to non-trivial unconstrained, continuous video data sets. Initially,
research advanced with the use of Gabor energy filters.
However, in recent work more attention has been given
to other features. Gabor energy filters lack generalization
needed in unconstrained situations. Additionally, they result
in an undesirably high feature vector dimensionality. Nontrivial
data sets have millions of samples; feature vectors must
be as low dimensional as possible. We propose a novel texture
feature based on Gabor energy filters that offers generalization
with a background texture suppression component and is
as compact as possible due to a maximal response representation
and local histograms. We improve performance on the
non-trivial Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2012 grandchallenge
data set.
Improving Action Units Recognition in Video
.png) We have developed a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition.
We start off by estimating the transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference face with canonical pose.
This initialization in our framework establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The affine
transformation computed from the initialization is then propagated by affine transformation estimated from the
dense optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-rigid facial appearance. We call this method
SIFT and optical flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic video-based face registration technique captures
the appearance changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state- of-the-art technique.
We have developed a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition.
We start off by estimating the transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference face with canonical pose.
This initialization in our framework establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The affine
transformation computed from the initialization is then propagated by affine transformation estimated from the
dense optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-rigid facial appearance. We call this method
SIFT and optical flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic video-based face registration technique captures
the appearance changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state- of-the-art technique.
Continuous Facial Emotion Recognition
 Affective computing -- the emergent field in which computers detect emotions and project appropriate
expressions of their own -- has reached a bottleneck where algorithms are not able to infer a person’s
emotions from natural and spontaneous facial expressions captured in video. We propose a principled method
which addresses the temporal dynamics of facial emotions and expressions in video with a sampling approach
inspired from human perceptual psychology. The method shows an
average improvement of 9.8% over the baseline for weighted accuracy on the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge
2011 video-based frame level sub-challenge testing set.
Affective computing -- the emergent field in which computers detect emotions and project appropriate
expressions of their own -- has reached a bottleneck where algorithms are not able to infer a person’s
emotions from natural and spontaneous facial expressions captured in video. We propose a principled method
which addresses the temporal dynamics of facial emotions and expressions in video with a sampling approach
inspired from human perceptual psychology. The method shows an
average improvement of 9.8% over the baseline for weighted accuracy on the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge
2011 video-based frame level sub-challenge testing set.
Improving Action Units Recognition Using Dense Flow-based Face Registration in Video
 Aligning faces with non-rigid muscle motion in
the real-world streaming video is a challenging problem. We
propose a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition. The registration
process is formulated as a dense SIFT-flow- and optical-flow-
based affine warping problem. We start off by estimating the
transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference
face with canonical pose. This initialization in our framework
establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The
affine transformation computed from the initialization is then
propagated by affine transformation estimated from the dense
optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-
rigid facial appearance. We call this method SIFT and optical
flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). This real-time algorithm
is designed for realistic streaming data, allowing us to analyze
the facial muscle dynamics in a meaningful manner. Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic
video-based face registration technique captures the appearance
changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state-
of-the-art technique.
Aligning faces with non-rigid muscle motion in
the real-world streaming video is a challenging problem. We
propose a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition. The registration
process is formulated as a dense SIFT-flow- and optical-flow-
based affine warping problem. We start off by estimating the
transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference
face with canonical pose. This initialization in our framework
establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The
affine transformation computed from the initialization is then
propagated by affine transformation estimated from the dense
optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-
rigid facial appearance. We call this method SIFT and optical
flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). This real-time algorithm
is designed for realistic streaming data, allowing us to analyze
the facial muscle dynamics in a meaningful manner. Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic
video-based face registration technique captures the appearance
changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state-
of-the-art technique.
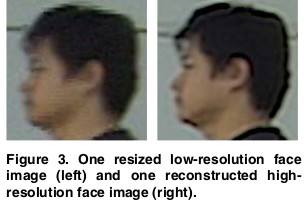
Face Image Super-Resolution using 2D CCA
 We have decveloped a face super-resolution method using two-dimensional canonical correlation analysis
(2D CCA) is presented. A detail compensation step is followed to add high-frequency components to the
reconstructed high-resolution face. In our approach the relationship between the
high-resolution and the low-resolution face image are maintained in their original 2D representation.
Different parts of a face image are super-resolved separately to better preserve the local structure.
The proposed method is compared with various state-of-the-art super-resolution algorithms.
The method is very efficient in both the training and testing phases compared to the other approaches.
We have decveloped a face super-resolution method using two-dimensional canonical correlation analysis
(2D CCA) is presented. A detail compensation step is followed to add high-frequency components to the
reconstructed high-resolution face. In our approach the relationship between the
high-resolution and the low-resolution face image are maintained in their original 2D representation.
Different parts of a face image are super-resolved separately to better preserve the local structure.
The proposed method is compared with various state-of-the-art super-resolution algorithms.
The method is very efficient in both the training and testing phases compared to the other approaches.
Understanding Discrete Facial Expressions in Video Using an EAI
 Existing video-based facial expression recognition techniques analyze the geometry-based and
appearance-based information in every frame as well as explore the temporal relation among frames.
On the contrary, we present a new image-based representation and an associated reference image called
the emotion avatar image (EAI), and the avatar reference, respectively.
The approach to facial expression analysis consists of
the following steps: 1) face detection; 2) face registration of video frames with the avatar reference to form the
EAI representation; 3) computation of features from EAIs using both local binary patterns and local phase
quantization; and 4) the classification of the feature as one of the emotion type by using a linear support
vector machine classifier. The experimental results demonstrate that the information captured in an EAI for a
facial expression is a very strong cue for emotion inference.
Existing video-based facial expression recognition techniques analyze the geometry-based and
appearance-based information in every frame as well as explore the temporal relation among frames.
On the contrary, we present a new image-based representation and an associated reference image called
the emotion avatar image (EAI), and the avatar reference, respectively.
The approach to facial expression analysis consists of
the following steps: 1) face detection; 2) face registration of video frames with the avatar reference to form the
EAI representation; 3) computation of features from EAIs using both local binary patterns and local phase
quantization; and 4) the classification of the feature as one of the emotion type by using a linear support
vector machine classifier. The experimental results demonstrate that the information captured in an EAI for a
facial expression is a very strong cue for emotion inference.
Facial Emotion Recognition With Expression Energy
 Facial emotion recognition
in unconstrained settings is a typical case where algorithms perform poorly. A property of the AVEC2012 data set
is that individuals in testing data are not encountered in training data. In these situations, conventional approaches
suffer because models developed from training data cannot properly discriminate unforeseen testing samples.
We propose
two similarity metrics that address the problems of a conventional approach: neutral similarity, measuring the
intensity of an expression; and temporal similarity, measuring changes in an expression over time. These
similarities are taken to be the energy of facial expressions.
Our method improves correlation by 35.5% over the baseline approach on the frame-level sub-challenge.
Facial emotion recognition
in unconstrained settings is a typical case where algorithms perform poorly. A property of the AVEC2012 data set
is that individuals in testing data are not encountered in training data. In these situations, conventional approaches
suffer because models developed from training data cannot properly discriminate unforeseen testing samples.
We propose
two similarity metrics that address the problems of a conventional approach: neutral similarity, measuring the
intensity of an expression; and temporal similarity, measuring changes in an expression over time. These
similarities are taken to be the energy of facial expressions.
Our method improves correlation by 35.5% over the baseline approach on the frame-level sub-challenge.
Cluster-Classification Bayesian Networks for Head Pose Estimation
 Head pose estimation is critical in many applications
such as face recognition and human-computer interaction.
Various classifiers such as LDA, SVM, or
nearest neighbor are widely used for this purpose; however,
the recognition rates are limited due to the limited
discriminative power of these classifiers for discretized
pose estimation. We propose a head
pose estimation method using a Cluster-Classification
Bayesian Network (CCBN), specifically designed for
classification after clustering. A pose layout is defined
where similar poses are assigned to the same block.
This increases the discriminative power within the same
block when similar yet different poses are present. We
achieve the highest recognition accuracy on two public
databases (CAS-PEAL and FEI) compared to the stateof-
the-art methods.
Head pose estimation is critical in many applications
such as face recognition and human-computer interaction.
Various classifiers such as LDA, SVM, or
nearest neighbor are widely used for this purpose; however,
the recognition rates are limited due to the limited
discriminative power of these classifiers for discretized
pose estimation. We propose a head
pose estimation method using a Cluster-Classification
Bayesian Network (CCBN), specifically designed for
classification after clustering. A pose layout is defined
where similar poses are assigned to the same block.
This increases the discriminative power within the same
block when similar yet different poses are present. We
achieve the highest recognition accuracy on two public
databases (CAS-PEAL and FEI) compared to the stateof-
the-art methods.
Face Recognition in Multi-Camera Surveillance Videos
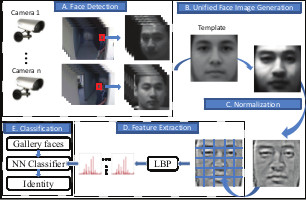 Recognizing faces in surveillance videos becomes
difficult due to the poor quality of the probe data in
terms of resolution, noise, blurriness, and varying light-
ing conditions. In addition, the poses of probe data are
usually not frontal view, contrary to the standard for-
mat of the gallery data. The discrepancy between the
two types of the data makes the existing recognition al-
gorithm less accurate in real-world data. In this pa-
per, we propose a multi-camera video based face recog-
nition framework using a novel image representation
called Unified Face Image (UFI), which is synthesized
from multiple camera feeds. Within a temporal window
the probe frames from different cameras are warped to-
wards a template frontal face and then averaged. The
generated UFI is a frontal view of the subject that in-
corporates information from different cameras. We use
SIFT flow as a high level alignment tool to warp the
faces. Experimental results show that by using the fused
face, the recognition performance is better than the re-
sult of any single camera. The proposed framework can
be adapted to any multi-camera video based recogni-
tion method using any feature descriptors or classifiers.
Recognizing faces in surveillance videos becomes
difficult due to the poor quality of the probe data in
terms of resolution, noise, blurriness, and varying light-
ing conditions. In addition, the poses of probe data are
usually not frontal view, contrary to the standard for-
mat of the gallery data. The discrepancy between the
two types of the data makes the existing recognition al-
gorithm less accurate in real-world data. In this pa-
per, we propose a multi-camera video based face recog-
nition framework using a novel image representation
called Unified Face Image (UFI), which is synthesized
from multiple camera feeds. Within a temporal window
the probe frames from different cameras are warped to-
wards a template frontal face and then averaged. The
generated UFI is a frontal view of the subject that in-
corporates information from different cameras. We use
SIFT flow as a high level alignment tool to warp the
faces. Experimental results show that by using the fused
face, the recognition performance is better than the re-
sult of any single camera. The proposed framework can
be adapted to any multi-camera video based recogni-
tion method using any feature descriptors or classifiers.
Face Recognition in Multi-Camera Surveillance Videos using Dynamic Bayesian Network
 38. In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
38. In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
Boosting Face Recognition in Real-World Surveillance Videos
.png) In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
A Biologically Inspired Approach for Fusing Facial Expression and
Appearance for Emotion Recognition
 Facial emotion recognition from video is an exemplar case
where both humans and computers underperform. In recent
emotion recognition competitions, top approaches were using
either geometric relationships that best captured facial dynamics
or an accurate registration technique to develop appearance
features. These two methods capture two different
types of facial information similarly to how the human visual
system divides information when perceiving faces. We propose a biologically-inspired fusion approach that
emulates this process. The efficacy of the approach is tested
with the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2011 data set, a
non-trivial data set where state-of-the-art approaches perform
under chance. The proposed approach increases classification
rates by 18.5% on publicly available data.
Facial emotion recognition from video is an exemplar case
where both humans and computers underperform. In recent
emotion recognition competitions, top approaches were using
either geometric relationships that best captured facial dynamics
or an accurate registration technique to develop appearance
features. These two methods capture two different
types of facial information similarly to how the human visual
system divides information when perceiving faces. We propose a biologically-inspired fusion approach that
emulates this process. The efficacy of the approach is tested
with the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2011 data set, a
non-trivial data set where state-of-the-art approaches perform
under chance. The proposed approach increases classification
rates by 18.5% on publicly available data.
A Psychologically-Inspired Match-Score Fusion Model for Video-Based Facial Expression Recognition
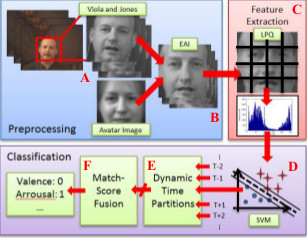 Communication between humans is rich in complexity and is not limited to verbal signals; emotions are
conveyed with gesture, pose and facial expression. Facial Emotion Recognition and Analysis (FERA),
the set of techniques by which non-verbal communication is quantified, is an exemplar case where humans
consistently outperform computer methods. While the field of FERA has seen many advances, no system
has been proposed which scales well to very large data sets. The challenge for computer vision is how to
automatically and non-heuristically downsample the data while maintaining a minimum representational
power that does not sacrifice accuracy. We propose a method inspired by human vision and
attention theory. Video is segmented into temporal partitions with a dynamic sampling rate based on the
frequency of visual information. Regions are homogenized by an experimentally selected match-score fusion
technique. The approach is shown to increase classification rates by over baseline with the AVEC 2011
video-subchallenge.
Communication between humans is rich in complexity and is not limited to verbal signals; emotions are
conveyed with gesture, pose and facial expression. Facial Emotion Recognition and Analysis (FERA),
the set of techniques by which non-verbal communication is quantified, is an exemplar case where humans
consistently outperform computer methods. While the field of FERA has seen many advances, no system
has been proposed which scales well to very large data sets. The challenge for computer vision is how to
automatically and non-heuristically downsample the data while maintaining a minimum representational
power that does not sacrifice accuracy. We propose a method inspired by human vision and
attention theory. Video is segmented into temporal partitions with a dynamic sampling rate based on the
frequency of visual information. Regions are homogenized by an experimentally selected match-score fusion
technique. The approach is shown to increase classification rates by over baseline with the AVEC 2011
video-subchallenge.
Facial Expression Recognition Using Emotion Avatar Image
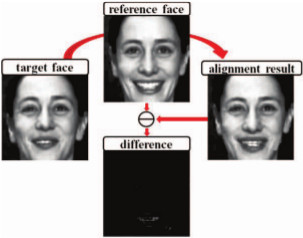 Existing facial expression recognition techniques
analyze the spatial and temporal information for every single
frame in a human emotion video. On the contrary, we create the
Emotion Avatar Image (EAI) as a single good representation for
each video or image sequence for emotion recognition. In this
paper, we adopt the recently introduced SIFT flow algorithm to
register every frame with respect to an Avatar reference face
model. Then, an iterative algorithm is used not only to superresolve
the EAI representation for each video and the Avatar
reference, but also to improve the recognition performance.
Subsequently, we extract the features from EAIs using both
Local Binary Pattern (LBP) and Local Phase Quantization
(LPQ). Then the results from both texture descriptors are tested
on the Facial Expression Recognition and Analysis Challenge
(FERA2011) data, GEMEP-FERA dataset. To evaluate this
simple yet powerful idea, we train our algorithm only using the
given 155 videos of training data from GEMEP-FERA dataset.
The result shows that our algorithm eliminates the personspecific
information for emotion and performs well on unseen
data.
Existing facial expression recognition techniques
analyze the spatial and temporal information for every single
frame in a human emotion video. On the contrary, we create the
Emotion Avatar Image (EAI) as a single good representation for
each video or image sequence for emotion recognition. In this
paper, we adopt the recently introduced SIFT flow algorithm to
register every frame with respect to an Avatar reference face
model. Then, an iterative algorithm is used not only to superresolve
the EAI representation for each video and the Avatar
reference, but also to improve the recognition performance.
Subsequently, we extract the features from EAIs using both
Local Binary Pattern (LBP) and Local Phase Quantization
(LPQ). Then the results from both texture descriptors are tested
on the Facial Expression Recognition and Analysis Challenge
(FERA2011) data, GEMEP-FERA dataset. To evaluate this
simple yet powerful idea, we train our algorithm only using the
given 155 videos of training data from GEMEP-FERA dataset.
The result shows that our algorithm eliminates the personspecific
information for emotion and performs well on unseen
data.
Face Recognition in Video with Closed-Loop Super-resolution
 Video-based face recognition has received significant attention in the past few years. However, the facial images
in a video sequence acquired from a distance are usually
small in size and their visual quality is low. Enhancing low-
resolution (LR) facial images from a video sequence is of
importance for performing face recognition. Registration is
a critical step in super-resolution (SR) of facial images from
a video which requires precise pose alignment and illumination normalization. Unlike traditional approaches that
perform tracking for each frame before using a SR method,
we present an incremental super-resolution
technique in which SR and tracking are linked together in
a closed-loop system. An incoming video frame is first registered in pose and normalized for illumination, and then
combined with the existing super-resolved texture. This
super-resolved texture, in turn, is used to improve the estimate of illumination and motion parameters for the next
frame. This process passes on the benefits of the SR result to
the tracking module and allows the entire system to reach its
potential. We show results on a low-resolution facial video.
We demonstrate a significant improvement in face recognition rates with the super-resolved images over the images
without super-resolution.
Video-based face recognition has received significant attention in the past few years. However, the facial images
in a video sequence acquired from a distance are usually
small in size and their visual quality is low. Enhancing low-
resolution (LR) facial images from a video sequence is of
importance for performing face recognition. Registration is
a critical step in super-resolution (SR) of facial images from
a video which requires precise pose alignment and illumination normalization. Unlike traditional approaches that
perform tracking for each frame before using a SR method,
we present an incremental super-resolution
technique in which SR and tracking are linked together in
a closed-loop system. An incoming video frame is first registered in pose and normalized for illumination, and then
combined with the existing super-resolved texture. This
super-resolved texture, in turn, is used to improve the estimate of illumination and motion parameters for the next
frame. This process passes on the benefits of the SR result to
the tracking module and allows the entire system to reach its
potential. We show results on a low-resolution facial video.
We demonstrate a significant improvement in face recognition rates with the super-resolved images over the images
without super-resolution.
Continuous learning of a multi-layered network topology in a video camera network
.png) A multilayered camera network architecture with nodes as entry/exit points, cameras, and clusters of cameras at different layers is proposed. This paper integrates face recognition that provides robustness to appearance changes and better models the time-varying traffic patterns in the network. The statistical dependence between the nodes, indicating the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, is represented by a weighted directed graph and transition times that may have multimodal distributions. The traffic patterns and the network topology may be changing in the dynamic environment. We propose a Monte Carlo Expectation-Maximization algorithm-based continuous learning mechanism to capture the latent dynamically changing characteristics of the network topology. In the experiments, a nine-camera network with twenty-five nodes (at the lowest level) is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments and compared with previous approaches.
A multilayered camera network architecture with nodes as entry/exit points, cameras, and clusters of cameras at different layers is proposed. This paper integrates face recognition that provides robustness to appearance changes and better models the time-varying traffic patterns in the network. The statistical dependence between the nodes, indicating the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, is represented by a weighted directed graph and transition times that may have multimodal distributions. The traffic patterns and the network topology may be changing in the dynamic environment. We propose a Monte Carlo Expectation-Maximization algorithm-based continuous learning mechanism to capture the latent dynamically changing characteristics of the network topology. In the experiments, a nine-camera network with twenty-five nodes (at the lowest level) is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments and compared with previous approaches.
Evaluating the Quality of Super-resolved Images for Face Recognition
 The widespread use of super-resolution methods, in a
variety of applications such as surveillance has led to
an increasing need for or quality assessment measures.
The current quality measures aim to compare different
fusion methods by assessing the quality of the fused images.
They consider the information transferred between
the super-resolved image and input images only. In this
paper, we propose an objective quality evaluation algorithm
for super-resolved images, which focuses on evaluating
the quality of super-resolved images that are constructed
from different conditions of input images. The
proposed quality evaluation method combines both the
relationship between the super-resolved image and the
input images, and the relationship between the input images.
Using the proposed measure, the quality of the
super-resolved face images constructed from videos are
evaluated under different conditions, including the variation
of pose, lighting, facial expressions and the number
of input images.
The widespread use of super-resolution methods, in a
variety of applications such as surveillance has led to
an increasing need for or quality assessment measures.
The current quality measures aim to compare different
fusion methods by assessing the quality of the fused images.
They consider the information transferred between
the super-resolved image and input images only. In this
paper, we propose an objective quality evaluation algorithm
for super-resolved images, which focuses on evaluating
the quality of super-resolved images that are constructed
from different conditions of input images. The
proposed quality evaluation method combines both the
relationship between the super-resolved image and the
input images, and the relationship between the input images.
Using the proposed measure, the quality of the
super-resolved face images constructed from videos are
evaluated under different conditions, including the variation
of pose, lighting, facial expressions and the number
of input images.
Super-resolution of Facial Images in Video with Expression Changes
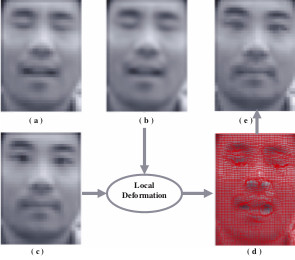 Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR
algorithms for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to
the SR process. However, the registration is a challenging
task for SR with expression changes. This research proposes a
new method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution
(LR) facial image by handling the facial image in a nonrigid
manner. It consists of global tracking, local alignment
for precise registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline
based Resolution Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation
(RAIFFD) model is used to recover a dense local nonrigid
flow field. In this scheme, low-resolution image model
is explicitly embedded in the optimization function formulation
to simulate the formation of low resolution image.
The results achieved by the proposed approach are significantly
better as compared to the SR approaches applied
on the whole face image without considering local deformations.
The results are also compared with two state-ofthe-
art SR algorithms to show the effectiveness of the approach
in super-resolving facial images with local expression
changes.
Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR
algorithms for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to
the SR process. However, the registration is a challenging
task for SR with expression changes. This research proposes a
new method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution
(LR) facial image by handling the facial image in a nonrigid
manner. It consists of global tracking, local alignment
for precise registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline
based Resolution Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation
(RAIFFD) model is used to recover a dense local nonrigid
flow field. In this scheme, low-resolution image model
is explicitly embedded in the optimization function formulation
to simulate the formation of low resolution image.
The results achieved by the proposed approach are significantly
better as compared to the SR approaches applied
on the whole face image without considering local deformations.
The results are also compared with two state-ofthe-
art SR algorithms to show the effectiveness of the approach
in super-resolving facial images with local expression
changes.
Super-Resolution of Deformed Facial Images in Video
 Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR algorithms
for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to the SR
process. However, the registration is a challenging task for
SR with expression changes. This research proposes a new
method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution (LR)
facial image by handling the facial image in a non-rigid manner.
It consists of global tracking, local alignment for precise
registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline based Resolution
Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation (RAIFFD) model
is used to recover a dense local non-rigid flow field. In this
scheme, low-resolution image model is explicitly embedded
in the optimization function formulation to simulate the formation
of low resolution image. The results achieved by the
proposed approach are significantly better as compared to
the SR approaches applied on the whole face image without
considering local deformations.
Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR algorithms
for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to the SR
process. However, the registration is a challenging task for
SR with expression changes. This research proposes a new
method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution (LR)
facial image by handling the facial image in a non-rigid manner.
It consists of global tracking, local alignment for precise
registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline based Resolution
Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation (RAIFFD) model
is used to recover a dense local non-rigid flow field. In this
scheme, low-resolution image model is explicitly embedded
in the optimization function formulation to simulate the formation
of low resolution image. The results achieved by the
proposed approach are significantly better as compared to
the SR approaches applied on the whole face image without
considering local deformations.
Feature fusion of side face and gait for video-based human identification
 Video-based human recognition at a distance remains a challenging problem for the fusion of multimodal
biometrics. We present a
new approach that utilizes and integrates information from side face and gait at the feature level. The features of
face and gait are obtained separately using principal component analysis (PCA) from enhanced side face image
(ESFI) and gait energy image (GEI), respectively. Multiple discriminant analysis (MDA) is employed on the
concatenated features of face and gait to obtain discriminating synthetic features. The experimental results demonstrate that the synthetic features, encoding both side face and gait
information, carry more discriminating power than the individual biometrics features, and the proposed feature
level fusion scheme outperforms the match score level and another feature level fusion scheme.
Video-based human recognition at a distance remains a challenging problem for the fusion of multimodal
biometrics. We present a
new approach that utilizes and integrates information from side face and gait at the feature level. The features of
face and gait are obtained separately using principal component analysis (PCA) from enhanced side face image
(ESFI) and gait energy image (GEI), respectively. Multiple discriminant analysis (MDA) is employed on the
concatenated features of face and gait to obtain discriminating synthetic features. The experimental results demonstrate that the synthetic features, encoding both side face and gait
information, carry more discriminating power than the individual biometrics features, and the proposed feature
level fusion scheme outperforms the match score level and another feature level fusion scheme.
Human Recognition at a Distance
.png) This paper consider face, side face, gait and ear and their possible fusion for human recognition. It presents an overview of some of the techniques that we have developed for (a) super-resoulution-based face recognition in video, (b) gait-based recognition in video, (c) fusion of super-resolved side face and gait in video, (d) ear recognition in color/range images, and (e) fusion performance prediction and validation. It presents various real-world examples to illustrate the ideas and points out the relative merits of the approaches that are discussed.
This paper consider face, side face, gait and ear and their possible fusion for human recognition. It presents an overview of some of the techniques that we have developed for (a) super-resoulution-based face recognition in video, (b) gait-based recognition in video, (c) fusion of super-resolved side face and gait in video, (d) ear recognition in color/range images, and (e) fusion performance prediction and validation. It presents various real-world examples to illustrate the ideas and points out the relative merits of the approaches that are discussed.
Integrating Face and Gait for Human Recognition at a Distance in Video
 We have introduced a new video-based recognition method to recognize noncooperating individuals at a
distance in video who expose side views to the camera. Information from two biometrics sources, side face
and gait, is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, an enhanced side-face image (ESFI), a
higher resolution image compared with the image directly obtained from a single video frame, is constructed.
For gait, the gait energy image (GEI),
a spatiotemporal compact representation of gait in video, is used to characterize human-walking properties.
The experimental results show that the idea of constructing
ESFI from multiple frames is promising for human recognition in video, and better face features are extracted
from ESFI compared to those from the original side-face images (OSFIs).
We have introduced a new video-based recognition method to recognize noncooperating individuals at a
distance in video who expose side views to the camera. Information from two biometrics sources, side face
and gait, is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, an enhanced side-face image (ESFI), a
higher resolution image compared with the image directly obtained from a single video frame, is constructed.
For gait, the gait energy image (GEI),
a spatiotemporal compact representation of gait in video, is used to characterize human-walking properties.
The experimental results show that the idea of constructing
ESFI from multiple frames is promising for human recognition in video, and better face features are extracted
from ESFI compared to those from the original side-face images (OSFIs).
Determining Topology in a Distributed Camera Network
.png) Recently, ‘entry/exit’ events of objects in the field-of-views of cameras were used to learn the topology of the camera network. The integration of object appearance was also proposed to employ the visual information provided by the imaging sensors. A problem with these methods is the lack of robustness to appearance changes. This paper integrates face recognition in the statistical model to better estimate the correspondence in the time-varying network. The statistical dependence between the entry and exit nodes indicates the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, which are represented by a weighted directed graph and transition time distributions. A nine-camera network with 25 nodes is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments, and compared with the previous approaches.
Recently, ‘entry/exit’ events of objects in the field-of-views of cameras were used to learn the topology of the camera network. The integration of object appearance was also proposed to employ the visual information provided by the imaging sensors. A problem with these methods is the lack of robustness to appearance changes. This paper integrates face recognition in the statistical model to better estimate the correspondence in the time-varying network. The statistical dependence between the entry and exit nodes indicates the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, which are represented by a weighted directed graph and transition time distributions. A nine-camera network with 25 nodes is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments, and compared with the previous approaches.
Super-resolved facial texture under changing pose and illumination
.png) In this paper, we propose a method to incrementally superresolve 3D facial texture by integrating information frame by frame from a video captured under changing poses and illuminations. First, we recover illumination, 3D motion and shape parameters from our tracking algorithm. This information is then used to super-resolve 3D texture using Iterative BackProjection (IBP) method. Finally, the super-resolved texture is fed back to the tracking part to improve the estimation of illumination and motion parameters. This closed-loop process continues to refine the texture as new frames come in. We also propose a local-region based scheme to handle non-rigidity of the human face. Experiments demonstrate that our framework not only incrementally super-resolves facial images, but recovers the detailed expression changes in high quality.
In this paper, we propose a method to incrementally superresolve 3D facial texture by integrating information frame by frame from a video captured under changing poses and illuminations. First, we recover illumination, 3D motion and shape parameters from our tracking algorithm. This information is then used to super-resolve 3D texture using Iterative BackProjection (IBP) method. Finally, the super-resolved texture is fed back to the tracking part to improve the estimation of illumination and motion parameters. This closed-loop process continues to refine the texture as new frames come in. We also propose a local-region based scheme to handle non-rigidity of the human face. Experiments demonstrate that our framework not only incrementally super-resolves facial images, but recovers the detailed expression changes in high quality.
Evolutionary Feature Synthesis for Facial Expression Recognition
 We present a novel genetically
inspired learning method for facial expression recognition (FER). Our learning method can select visually meaningful
features automatically in a genetic programming-based approach that uses Gabor wavelet representation for
primitive features and linear/nonlinear operators to synthesize new features. To make use of random nature of a genetic
program, we design a multi-agent scheme to boost the performance. We compare the performance of our
approach with several approaches in the literature and show that our approach can perform the task of facial
expression recognition effectively.
We present a novel genetically
inspired learning method for facial expression recognition (FER). Our learning method can select visually meaningful
features automatically in a genetic programming-based approach that uses Gabor wavelet representation for
primitive features and linear/nonlinear operators to synthesize new features. To make use of random nature of a genetic
program, we design a multi-agent scheme to boost the performance. We compare the performance of our
approach with several approaches in the literature and show that our approach can perform the task of facial
expression recognition effectively.
Feature Fusion of Face and Gait for Human Recognition at a Distance in Video
 A new video based recognition method is presented
to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance in
video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait, is utilized
and integrated at feature level. For face, a high-resolution
side face image is constructed from multiple video frames.
For gait, Gait Energy Image (GEI), a spatio-temporal compact
representation of gait in video, is used to characterize
human walking properties. Face features and gait features
are obtained separately using Principal Component Analysis
(PCA) and Multiple Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined
method from the high-resolution side face image and
Gait Energy Image (GEI), respectively. The system is tested
on a database of video sequences corresponding to 46 people.
The results showed that the integrated face and gait
features carry the most discriminating power compared to
any individual biometric.
A new video based recognition method is presented
to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance in
video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait, is utilized
and integrated at feature level. For face, a high-resolution
side face image is constructed from multiple video frames.
For gait, Gait Energy Image (GEI), a spatio-temporal compact
representation of gait in video, is used to characterize
human walking properties. Face features and gait features
are obtained separately using Principal Component Analysis
(PCA) and Multiple Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined
method from the high-resolution side face image and
Gait Energy Image (GEI), respectively. The system is tested
on a database of video sequences corresponding to 46 people.
The results showed that the integrated face and gait
features carry the most discriminating power compared to
any individual biometric.
Super-resolution Restoration of Facial Images in Video
 Reconstruction-based super-resolution has been widely
treated in computer vision. However, super-resolution of
facial images has received very little attention. Since different
parts of a face may have different motions in normal
videos, we propose a new method for enhancing
the resolution of low-resolution facial image by handling
the facial image non-uniformly. We divide low-resolution
face image into different regions based on facial features
and estimate motions of each of these regions using different
motion models. Our experimental results show we can
achieve better results than applying super-resolution on the
whole face image uniformly.
Reconstruction-based super-resolution has been widely
treated in computer vision. However, super-resolution of
facial images has received very little attention. Since different
parts of a face may have different motions in normal
videos, we propose a new method for enhancing
the resolution of low-resolution facial image by handling
the facial image non-uniformly. We divide low-resolution
face image into different regions based on facial features
and estimate motions of each of these regions using different
motion models. Our experimental results show we can
achieve better results than applying super-resolution on the
whole face image uniformly.
Integrating Face and Gait for Human Recognition
 We introduce a new video based recognition
method to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance
in video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait,
is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, we
construct Enhanced Side Face Image (ESFI), a higher resolution
image compared with the image directly obtained
from a single video frame, to fuse information of face from
multiple video frames. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image
(GEI), a spatio-temporal compact representation of gait in
video, to characterize human walking properties. The features
of face and the features of gait are obtained separately
using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Multiple
Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined method from ESFI
and GEI, respectively. They are then integrated at match
score level. Our approach is tested on a database of video
sequences corresponding to 46 people. The different fusion
methods are compared and analyzed. The experimental results
show that (a) Integrated information from side face
and gait is effective for human recognition in video; (b) The
idea of constructing ESFI from multiple frames is promising
for human recognition in video and better face features are
extracted from ESFI compared to those from original face
images.
We introduce a new video based recognition
method to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance
in video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait,
is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, we
construct Enhanced Side Face Image (ESFI), a higher resolution
image compared with the image directly obtained
from a single video frame, to fuse information of face from
multiple video frames. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image
(GEI), a spatio-temporal compact representation of gait in
video, to characterize human walking properties. The features
of face and the features of gait are obtained separately
using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Multiple
Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined method from ESFI
and GEI, respectively. They are then integrated at match
score level. Our approach is tested on a database of video
sequences corresponding to 46 people. The different fusion
methods are compared and analyzed. The experimental results
show that (a) Integrated information from side face
and gait is effective for human recognition in video; (b) The
idea of constructing ESFI from multiple frames is promising
for human recognition in video and better face features are
extracted from ESFI compared to those from original face
images.
Human recognition at a distance in video by integrating face profile and gait
.png) Human recognition from arbitrary views is an important task for many applications, such as visual surveillance, covert security and access control. It has been found to be very difficult in reality, especially when a person is walking at a distance in read-world outdoor conditions. For optimal performance, the system should use as much information as possible from the observations. In this paper, we propose an innovative system, which combines cues of face profile and gait silhouette from the single camera video sequences. For optimal face profile recognition, we first reconstruct a high-resolution face profile image from several adjacent low-resolution video frames. Then we use a curvature-based matching method for recognition. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image (GEI) to characterize human walking properties. Recognition is carried out based on the direct GEI matching. Several schemes are considered for fusion of face profile and gait. A number of dynamic video sequences are tested to evaluate the performance of our system. Experiment results are compared and discussed.
Human recognition from arbitrary views is an important task for many applications, such as visual surveillance, covert security and access control. It has been found to be very difficult in reality, especially when a person is walking at a distance in read-world outdoor conditions. For optimal performance, the system should use as much information as possible from the observations. In this paper, we propose an innovative system, which combines cues of face profile and gait silhouette from the single camera video sequences. For optimal face profile recognition, we first reconstruct a high-resolution face profile image from several adjacent low-resolution video frames. Then we use a curvature-based matching method for recognition. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image (GEI) to characterize human walking properties. Recognition is carried out based on the direct GEI matching. Several schemes are considered for fusion of face profile and gait. A number of dynamic video sequences are tested to evaluate the performance of our system. Experiment results are compared and discussed.
Human Recognition Based on Face Profiles in Video
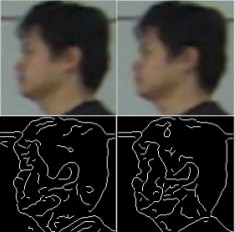 Face profile is an important aspect of face recognition and
it provides a complementary structure of the face that is
seen in the non-frontal view. In the past, several methods
have been proposed to recognize face profiles in still images.
However, face profile images that are captured at
a distance by surveillance cameras usually are video sequences
that have a low resolution. It is difficult to extract
accurate face profile directly from a low-resolution video
frame, which does not have many pixels on the face profile.
The emphasis of this research is to introduce a practical approach
for human recognition by using high-resolution face
profile images constructed from the low-resolution videos.
We use both the spatial and temporal information present
in a number of adjacent low-resolution frames of a video
sequence to construct high-resolution face profile images.
As the quality of high-resolution images relies on the correctness
of image alignment between consecutive frames,
an elastic registration algorithm is used for face profile image
alignment. A match statistic is designed to detect and
discard poorly aligned images which may degrade the quality
of the high-resolution face profile image. After obtaining
high-resolution face profile images, we use a dynamic time
warping method for face profile recognition. A number of
dynamic video sequences are tested to demonstrate the applicability
and reliability of our method.
Face profile is an important aspect of face recognition and
it provides a complementary structure of the face that is
seen in the non-frontal view. In the past, several methods
have been proposed to recognize face profiles in still images.
However, face profile images that are captured at
a distance by surveillance cameras usually are video sequences
that have a low resolution. It is difficult to extract
accurate face profile directly from a low-resolution video
frame, which does not have many pixels on the face profile.
The emphasis of this research is to introduce a practical approach
for human recognition by using high-resolution face
profile images constructed from the low-resolution videos.
We use both the spatial and temporal information present
in a number of adjacent low-resolution frames of a video
sequence to construct high-resolution face profile images.
As the quality of high-resolution images relies on the correctness
of image alignment between consecutive frames,
an elastic registration algorithm is used for face profile image
alignment. A match statistic is designed to detect and
discard poorly aligned images which may degrade the quality
of the high-resolution face profile image. After obtaining
high-resolution face profile images, we use a dynamic time
warping method for face profile recognition. A number of
dynamic video sequences are tested to demonstrate the applicability
and reliability of our method.
Face Recognition from Face Profile Using Dynamic Time Warping
 Most of the current profile recognition algorithms
depend on the correct detection of fiducial points and the
determination of relationships among these fiducial
points. Unfortunately, some features such as concave
nose, protruding lips, flat chin, etc., make detection of
such points difficult and unreliable. Also, the number and
position of fiducial points vary when expression changes
even for the same person. A curvature based
matching approach is presented in this research, which does not
require the extraction of all the fiducial points, but uses
information contained in the profile. The scale space
filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the
curvature of the filtered profile is computed. Using the
curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple
method. Then a dynamic time warping method is applied
to match the face profile portion from nasion to throat
based on the curvature value. Experiments are performed
on two profile face image databases. Recognition rates
and conclusion are presented and discussed.
Most of the current profile recognition algorithms
depend on the correct detection of fiducial points and the
determination of relationships among these fiducial
points. Unfortunately, some features such as concave
nose, protruding lips, flat chin, etc., make detection of
such points difficult and unreliable. Also, the number and
position of fiducial points vary when expression changes
even for the same person. A curvature based
matching approach is presented in this research, which does not
require the extraction of all the fiducial points, but uses
information contained in the profile. The scale space
filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the
curvature of the filtered profile is computed. Using the
curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple
method. Then a dynamic time warping method is applied
to match the face profile portion from nasion to throat
based on the curvature value. Experiments are performed
on two profile face image databases. Recognition rates
and conclusion are presented and discussed.
Face Recognition from Face Profile Using Dynamic Time Warping
 We present a curvature-based matching approach, which uses information contained in
the facial profile. The scale space filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the curvature of the
filtered profile is computed. Using the curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple method. Then a dynamic time warping method
is applied. Experiments are performed on two profile face image databases.
We present a curvature-based matching approach, which uses information contained in
the facial profile. The scale space filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the curvature of the
filtered profile is computed. Using the curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple method. Then a dynamic time warping method
is applied. Experiments are performed on two profile face image databases.
Feature Synthesis Using Genetic Programming for Face Expression Recognition
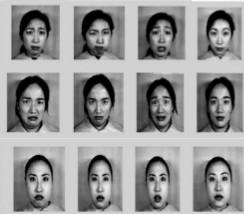 We introduce a novel genetically-inspired learning method for face expression recognition (FER) in visible images. Unlike
current research for FER that generally uses visually meaningful feature, we
proposed a Genetic Programming based technique, which learns to discover
composite operators and features that are evolved from combinations of
primitive image processing operations. In this approach, the output of the
learned composite operator is a feature vector that is used for FER. The
experimental results show that our approach can find good composite operators
to effectively extract useful features.
We introduce a novel genetically-inspired learning method for face expression recognition (FER) in visible images. Unlike
current research for FER that generally uses visually meaningful feature, we
proposed a Genetic Programming based technique, which learns to discover
composite operators and features that are evolved from combinations of
primitive image processing operations. In this approach, the output of the
learned composite operator is a feature vector that is used for FER. The
experimental results show that our approach can find good composite operators
to effectively extract useful features.
|


.png) The focus of this paper is on presentation attack detection for the iris biometrics, which measures the pattern within the colored concentric circle of the subjects’ eyes, to authenticate an individual to a generic user verification system. Unlike previous deep learning methods that use single convolutional neural network architectures, this paper develops a framework built upon triplet convolutional networks that takes as input two real iris patches and a fake patch or two fake patches and a genuine patch. The smaller architecture provides a way to do early stopping based on the liveness of single patches rather than the whole image. The matching is performed by computing the distance with respect to a reference set of real and fake examples. The proposed approach allows for realtime processing using a smaller network and provides equal or better than state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets of photo-based and contact lens presentation attacks.
The focus of this paper is on presentation attack detection for the iris biometrics, which measures the pattern within the colored concentric circle of the subjects’ eyes, to authenticate an individual to a generic user verification system. Unlike previous deep learning methods that use single convolutional neural network architectures, this paper develops a framework built upon triplet convolutional networks that takes as input two real iris patches and a fake patch or two fake patches and a genuine patch. The smaller architecture provides a way to do early stopping based on the liveness of single patches rather than the whole image. The matching is performed by computing the distance with respect to a reference set of real and fake examples. The proposed approach allows for realtime processing using a smaller network and provides equal or better than state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets of photo-based and contact lens presentation attacks.
 Face recognition has been studied extensively; however, real-world face recognition still remains a
challenging task. We approach face recognition in the context of graph theory. We recognize an unknown face
using an external Reference Face Graph (RFG). A RFG is generated and recognition of a given face is achieved
by comparing it to the faces in the constructed RFG. The results show that the proposed approach outperforms
the state-of-the-art methods.
Face recognition has been studied extensively; however, real-world face recognition still remains a
challenging task. We approach face recognition in the context of graph theory. We recognize an unknown face
using an external Reference Face Graph (RFG). A RFG is generated and recognition of a given face is achieved
by comparing it to the faces in the constructed RFG. The results show that the proposed approach outperforms
the state-of-the-art methods.
.png) Facial biometrics is a multidisciplinary field based on the methods and technologies of image analysis and machine learning, as applied to identifying people from facial information, and has progressed for over three decades in terms of theory, algorithms, and applications. While surveillance systems are in common practice and close-range facial recognition at entry points exist, the field has progressed beyond still image recognition in controlled imaging environments. In general, face recognition in the wild connotes recognition from still images and videos, unabated by age, pose, illumination, and expression (A-PIE) of individuals.
Facial biometrics is a multidisciplinary field based on the methods and technologies of image analysis and machine learning, as applied to identifying people from facial information, and has progressed for over three decades in terms of theory, algorithms, and applications. While surveillance systems are in common practice and close-range facial recognition at entry points exist, the field has progressed beyond still image recognition in controlled imaging environments. In general, face recognition in the wild connotes recognition from still images and videos, unabated by age, pose, illumination, and expression (A-PIE) of individuals.
![Sample images from LFW [44],FERET [40], RaFD [42], BioID [43],FEI [41], and Multi-PIE [39]](../research_images/DiscreteCosineTransformLocality-SensitiveHashes14.png) Searching large databases using local binary patterns for face recognition has been problematic due to
the cost of the linear search, and the inadequate performance of existing indexing
methods. We present Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) hashing for creating index structures for
face descriptors. Hashes play the role of keywords: an index is created, and queried to find
the images most similar to the query image. It is shown here that DCT hashing has significantly
better retrieval accuracy and it is more efficient compared to other popular state-of-the-art
hash algorithms.
Searching large databases using local binary patterns for face recognition has been problematic due to
the cost of the linear search, and the inadequate performance of existing indexing
methods. We present Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) hashing for creating index structures for
face descriptors. Hashes play the role of keywords: an index is created, and queried to find
the images most similar to the query image. It is shown here that DCT hashing has significantly
better retrieval accuracy and it is more efficient compared to other popular state-of-the-art
hash algorithms.
 Achieving good performance in surveillance videos with unconstrained faces is inherently difficult.
We aim at tackling this unconstrained face recognition problem and utilizing multiple cameras to improve the recognition
accuracy using a probabilistic approach.
The proposed method is tested on a public surveillance video dataset with a three-camera setup.
We compare our method to different benchmark classifiers with various feature descriptors.
The results demonstrate that by modeling the face in a dynamic manner the recognition performance
in a multi-camera network is improved and the recognition result is better than using any of the single cameras.
Achieving good performance in surveillance videos with unconstrained faces is inherently difficult.
We aim at tackling this unconstrained face recognition problem and utilizing multiple cameras to improve the recognition
accuracy using a probabilistic approach.
The proposed method is tested on a public surveillance video dataset with a three-camera setup.
We compare our method to different benchmark classifiers with various feature descriptors.
The results demonstrate that by modeling the face in a dynamic manner the recognition performance
in a multi-camera network is improved and the recognition result is better than using any of the single cameras.
 State-of-the-art approaches have yet to deliver a feature representation
for facial emotion recognition that can be applied
to non-trivial unconstrained, continuous video data sets. Initially,
research advanced with the use of Gabor energy filters.
However, in recent work more attention has been given
to other features. Gabor energy filters lack generalization
needed in unconstrained situations. Additionally, they result
in an undesirably high feature vector dimensionality. Nontrivial
data sets have millions of samples; feature vectors must
be as low dimensional as possible. We propose a novel texture
feature based on Gabor energy filters that offers generalization
with a background texture suppression component and is
as compact as possible due to a maximal response representation
and local histograms. We improve performance on the
non-trivial Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2012 grandchallenge
data set.
State-of-the-art approaches have yet to deliver a feature representation
for facial emotion recognition that can be applied
to non-trivial unconstrained, continuous video data sets. Initially,
research advanced with the use of Gabor energy filters.
However, in recent work more attention has been given
to other features. Gabor energy filters lack generalization
needed in unconstrained situations. Additionally, they result
in an undesirably high feature vector dimensionality. Nontrivial
data sets have millions of samples; feature vectors must
be as low dimensional as possible. We propose a novel texture
feature based on Gabor energy filters that offers generalization
with a background texture suppression component and is
as compact as possible due to a maximal response representation
and local histograms. We improve performance on the
non-trivial Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2012 grandchallenge
data set.
.png) We have developed a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition.
We start off by estimating the transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference face with canonical pose.
This initialization in our framework establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The affine
transformation computed from the initialization is then propagated by affine transformation estimated from the
dense optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-rigid facial appearance. We call this method
SIFT and optical flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic video-based face registration technique captures
the appearance changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state- of-the-art technique.
We have developed a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition.
We start off by estimating the transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference face with canonical pose.
This initialization in our framework establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The affine
transformation computed from the initialization is then propagated by affine transformation estimated from the
dense optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-rigid facial appearance. We call this method
SIFT and optical flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic video-based face registration technique captures
the appearance changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state- of-the-art technique.
 Affective computing -- the emergent field in which computers detect emotions and project appropriate
expressions of their own -- has reached a bottleneck where algorithms are not able to infer a person’s
emotions from natural and spontaneous facial expressions captured in video. We propose a principled method
which addresses the temporal dynamics of facial emotions and expressions in video with a sampling approach
inspired from human perceptual psychology. The method shows an
average improvement of 9.8% over the baseline for weighted accuracy on the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge
2011 video-based frame level sub-challenge testing set.
Affective computing -- the emergent field in which computers detect emotions and project appropriate
expressions of their own -- has reached a bottleneck where algorithms are not able to infer a person’s
emotions from natural and spontaneous facial expressions captured in video. We propose a principled method
which addresses the temporal dynamics of facial emotions and expressions in video with a sampling approach
inspired from human perceptual psychology. The method shows an
average improvement of 9.8% over the baseline for weighted accuracy on the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge
2011 video-based frame level sub-challenge testing set.
 Aligning faces with non-rigid muscle motion in
the real-world streaming video is a challenging problem. We
propose a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition. The registration
process is formulated as a dense SIFT-flow- and optical-flow-
based affine warping problem. We start off by estimating the
transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference
face with canonical pose. This initialization in our framework
establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The
affine transformation computed from the initialization is then
propagated by affine transformation estimated from the dense
optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-
rigid facial appearance. We call this method SIFT and optical
flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). This real-time algorithm
is designed for realistic streaming data, allowing us to analyze
the facial muscle dynamics in a meaningful manner. Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic
video-based face registration technique captures the appearance
changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state-
of-the-art technique.
Aligning faces with non-rigid muscle motion in
the real-world streaming video is a challenging problem. We
propose a novel automatic video-based face registration architecture for facial expression recognition. The registration
process is formulated as a dense SIFT-flow- and optical-flow-
based affine warping problem. We start off by estimating the
transformation of an arbitrary face to a generic reference
face with canonical pose. This initialization in our framework
establishes a head pose and person independent face model. The
affine transformation computed from the initialization is then
propagated by affine transformation estimated from the dense
optical flow to guarantee the temporal smoothness of the non-
rigid facial appearance. We call this method SIFT and optical
flow affine image transform (SOFAIT). This real-time algorithm
is designed for realistic streaming data, allowing us to analyze
the facial muscle dynamics in a meaningful manner. Visual and
quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed automatic
video-based face registration technique captures the appearance
changes in spontaneous expressions and outperforms the state-
of-the-art technique.
 We have decveloped a face super-resolution method using two-dimensional canonical correlation analysis
(2D CCA) is presented. A detail compensation step is followed to add high-frequency components to the
reconstructed high-resolution face. In our approach the relationship between the
high-resolution and the low-resolution face image are maintained in their original 2D representation.
Different parts of a face image are super-resolved separately to better preserve the local structure.
The proposed method is compared with various state-of-the-art super-resolution algorithms.
The method is very efficient in both the training and testing phases compared to the other approaches.
We have decveloped a face super-resolution method using two-dimensional canonical correlation analysis
(2D CCA) is presented. A detail compensation step is followed to add high-frequency components to the
reconstructed high-resolution face. In our approach the relationship between the
high-resolution and the low-resolution face image are maintained in their original 2D representation.
Different parts of a face image are super-resolved separately to better preserve the local structure.
The proposed method is compared with various state-of-the-art super-resolution algorithms.
The method is very efficient in both the training and testing phases compared to the other approaches.
 Existing video-based facial expression recognition techniques analyze the geometry-based and
appearance-based information in every frame as well as explore the temporal relation among frames.
On the contrary, we present a new image-based representation and an associated reference image called
the emotion avatar image (EAI), and the avatar reference, respectively.
The approach to facial expression analysis consists of
the following steps: 1) face detection; 2) face registration of video frames with the avatar reference to form the
EAI representation; 3) computation of features from EAIs using both local binary patterns and local phase
quantization; and 4) the classification of the feature as one of the emotion type by using a linear support
vector machine classifier. The experimental results demonstrate that the information captured in an EAI for a
facial expression is a very strong cue for emotion inference.
Existing video-based facial expression recognition techniques analyze the geometry-based and
appearance-based information in every frame as well as explore the temporal relation among frames.
On the contrary, we present a new image-based representation and an associated reference image called
the emotion avatar image (EAI), and the avatar reference, respectively.
The approach to facial expression analysis consists of
the following steps: 1) face detection; 2) face registration of video frames with the avatar reference to form the
EAI representation; 3) computation of features from EAIs using both local binary patterns and local phase
quantization; and 4) the classification of the feature as one of the emotion type by using a linear support
vector machine classifier. The experimental results demonstrate that the information captured in an EAI for a
facial expression is a very strong cue for emotion inference.
 Facial emotion recognition
in unconstrained settings is a typical case where algorithms perform poorly. A property of the AVEC2012 data set
is that individuals in testing data are not encountered in training data. In these situations, conventional approaches
suffer because models developed from training data cannot properly discriminate unforeseen testing samples.
We propose
two similarity metrics that address the problems of a conventional approach: neutral similarity, measuring the
intensity of an expression; and temporal similarity, measuring changes in an expression over time. These
similarities are taken to be the energy of facial expressions.
Our method improves correlation by 35.5% over the baseline approach on the frame-level sub-challenge.
Facial emotion recognition
in unconstrained settings is a typical case where algorithms perform poorly. A property of the AVEC2012 data set
is that individuals in testing data are not encountered in training data. In these situations, conventional approaches
suffer because models developed from training data cannot properly discriminate unforeseen testing samples.
We propose
two similarity metrics that address the problems of a conventional approach: neutral similarity, measuring the
intensity of an expression; and temporal similarity, measuring changes in an expression over time. These
similarities are taken to be the energy of facial expressions.
Our method improves correlation by 35.5% over the baseline approach on the frame-level sub-challenge.
 Head pose estimation is critical in many applications
such as face recognition and human-computer interaction.
Various classifiers such as LDA, SVM, or
nearest neighbor are widely used for this purpose; however,
the recognition rates are limited due to the limited
discriminative power of these classifiers for discretized
pose estimation. We propose a head
pose estimation method using a Cluster-Classification
Bayesian Network (CCBN), specifically designed for
classification after clustering. A pose layout is defined
where similar poses are assigned to the same block.
This increases the discriminative power within the same
block when similar yet different poses are present. We
achieve the highest recognition accuracy on two public
databases (CAS-PEAL and FEI) compared to the stateof-
the-art methods.
Head pose estimation is critical in many applications
such as face recognition and human-computer interaction.
Various classifiers such as LDA, SVM, or
nearest neighbor are widely used for this purpose; however,
the recognition rates are limited due to the limited
discriminative power of these classifiers for discretized
pose estimation. We propose a head
pose estimation method using a Cluster-Classification
Bayesian Network (CCBN), specifically designed for
classification after clustering. A pose layout is defined
where similar poses are assigned to the same block.
This increases the discriminative power within the same
block when similar yet different poses are present. We
achieve the highest recognition accuracy on two public
databases (CAS-PEAL and FEI) compared to the stateof-
the-art methods.
 Recognizing faces in surveillance videos becomes
difficult due to the poor quality of the probe data in
terms of resolution, noise, blurriness, and varying light-
ing conditions. In addition, the poses of probe data are
usually not frontal view, contrary to the standard for-
mat of the gallery data. The discrepancy between the
two types of the data makes the existing recognition al-
gorithm less accurate in real-world data. In this pa-
per, we propose a multi-camera video based face recog-
nition framework using a novel image representation
called Unified Face Image (UFI), which is synthesized
from multiple camera feeds. Within a temporal window
the probe frames from different cameras are warped to-
wards a template frontal face and then averaged. The
generated UFI is a frontal view of the subject that in-
corporates information from different cameras. We use
SIFT flow as a high level alignment tool to warp the
faces. Experimental results show that by using the fused
face, the recognition performance is better than the re-
sult of any single camera. The proposed framework can
be adapted to any multi-camera video based recogni-
tion method using any feature descriptors or classifiers.
Recognizing faces in surveillance videos becomes
difficult due to the poor quality of the probe data in
terms of resolution, noise, blurriness, and varying light-
ing conditions. In addition, the poses of probe data are
usually not frontal view, contrary to the standard for-
mat of the gallery data. The discrepancy between the
two types of the data makes the existing recognition al-
gorithm less accurate in real-world data. In this pa-
per, we propose a multi-camera video based face recog-
nition framework using a novel image representation
called Unified Face Image (UFI), which is synthesized
from multiple camera feeds. Within a temporal window
the probe frames from different cameras are warped to-
wards a template frontal face and then averaged. The
generated UFI is a frontal view of the subject that in-
corporates information from different cameras. We use
SIFT flow as a high level alignment tool to warp the
faces. Experimental results show that by using the fused
face, the recognition performance is better than the re-
sult of any single camera. The proposed framework can
be adapted to any multi-camera video based recogni-
tion method using any feature descriptors or classifiers.
 38. In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
38. In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
.png) In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
In this paper, we propose a video based face recognition framework using a novel image representation called warped average face (WAF). The WAFs are generated in two stages: in-sequence warping and frontal view warping. The WAFs can be easily used with various feature descriptors or classifiers. As compared to the original probe data, the image quality of the WAFs is significantly better and the appearance difference between the WAFs and the gallery data is suppressed. Given a probe sequence, only a few WAFs need to be generated for the recognition purpose. We test the proposed method on the ChokePoint dataset and our in-house dataset of surveillance quality. Experiments show that with the new image representation, the recognition accuracy can be boosted significantly.
 Facial emotion recognition from video is an exemplar case
where both humans and computers underperform. In recent
emotion recognition competitions, top approaches were using
either geometric relationships that best captured facial dynamics
or an accurate registration technique to develop appearance
features. These two methods capture two different
types of facial information similarly to how the human visual
system divides information when perceiving faces. We propose a biologically-inspired fusion approach that
emulates this process. The efficacy of the approach is tested
with the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2011 data set, a
non-trivial data set where state-of-the-art approaches perform
under chance. The proposed approach increases classification
rates by 18.5% on publicly available data.
Facial emotion recognition from video is an exemplar case
where both humans and computers underperform. In recent
emotion recognition competitions, top approaches were using
either geometric relationships that best captured facial dynamics
or an accurate registration technique to develop appearance
features. These two methods capture two different
types of facial information similarly to how the human visual
system divides information when perceiving faces. We propose a biologically-inspired fusion approach that
emulates this process. The efficacy of the approach is tested
with the Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2011 data set, a
non-trivial data set where state-of-the-art approaches perform
under chance. The proposed approach increases classification
rates by 18.5% on publicly available data.
 Communication between humans is rich in complexity and is not limited to verbal signals; emotions are
conveyed with gesture, pose and facial expression. Facial Emotion Recognition and Analysis (FERA),
the set of techniques by which non-verbal communication is quantified, is an exemplar case where humans
consistently outperform computer methods. While the field of FERA has seen many advances, no system
has been proposed which scales well to very large data sets. The challenge for computer vision is how to
automatically and non-heuristically downsample the data while maintaining a minimum representational
power that does not sacrifice accuracy. We propose a method inspired by human vision and
attention theory. Video is segmented into temporal partitions with a dynamic sampling rate based on the
frequency of visual information. Regions are homogenized by an experimentally selected match-score fusion
technique. The approach is shown to increase classification rates by over baseline with the AVEC 2011
video-subchallenge.
Communication between humans is rich in complexity and is not limited to verbal signals; emotions are
conveyed with gesture, pose and facial expression. Facial Emotion Recognition and Analysis (FERA),
the set of techniques by which non-verbal communication is quantified, is an exemplar case where humans
consistently outperform computer methods. While the field of FERA has seen many advances, no system
has been proposed which scales well to very large data sets. The challenge for computer vision is how to
automatically and non-heuristically downsample the data while maintaining a minimum representational
power that does not sacrifice accuracy. We propose a method inspired by human vision and
attention theory. Video is segmented into temporal partitions with a dynamic sampling rate based on the
frequency of visual information. Regions are homogenized by an experimentally selected match-score fusion
technique. The approach is shown to increase classification rates by over baseline with the AVEC 2011
video-subchallenge.
 Existing facial expression recognition techniques
analyze the spatial and temporal information for every single
frame in a human emotion video. On the contrary, we create the
Emotion Avatar Image (EAI) as a single good representation for
each video or image sequence for emotion recognition. In this
paper, we adopt the recently introduced SIFT flow algorithm to
register every frame with respect to an Avatar reference face
model. Then, an iterative algorithm is used not only to superresolve
the EAI representation for each video and the Avatar
reference, but also to improve the recognition performance.
Subsequently, we extract the features from EAIs using both
Local Binary Pattern (LBP) and Local Phase Quantization
(LPQ). Then the results from both texture descriptors are tested
on the Facial Expression Recognition and Analysis Challenge
(FERA2011) data, GEMEP-FERA dataset. To evaluate this
simple yet powerful idea, we train our algorithm only using the
given 155 videos of training data from GEMEP-FERA dataset.
The result shows that our algorithm eliminates the personspecific
information for emotion and performs well on unseen
data.
Existing facial expression recognition techniques
analyze the spatial and temporal information for every single
frame in a human emotion video. On the contrary, we create the
Emotion Avatar Image (EAI) as a single good representation for
each video or image sequence for emotion recognition. In this
paper, we adopt the recently introduced SIFT flow algorithm to
register every frame with respect to an Avatar reference face
model. Then, an iterative algorithm is used not only to superresolve
the EAI representation for each video and the Avatar
reference, but also to improve the recognition performance.
Subsequently, we extract the features from EAIs using both
Local Binary Pattern (LBP) and Local Phase Quantization
(LPQ). Then the results from both texture descriptors are tested
on the Facial Expression Recognition and Analysis Challenge
(FERA2011) data, GEMEP-FERA dataset. To evaluate this
simple yet powerful idea, we train our algorithm only using the
given 155 videos of training data from GEMEP-FERA dataset.
The result shows that our algorithm eliminates the personspecific
information for emotion and performs well on unseen
data.
 Video-based face recognition has received significant attention in the past few years. However, the facial images
in a video sequence acquired from a distance are usually
small in size and their visual quality is low. Enhancing low-
resolution (LR) facial images from a video sequence is of
importance for performing face recognition. Registration is
a critical step in super-resolution (SR) of facial images from
a video which requires precise pose alignment and illumination normalization. Unlike traditional approaches that
perform tracking for each frame before using a SR method,
we present an incremental super-resolution
technique in which SR and tracking are linked together in
a closed-loop system. An incoming video frame is first registered in pose and normalized for illumination, and then
combined with the existing super-resolved texture. This
super-resolved texture, in turn, is used to improve the estimate of illumination and motion parameters for the next
frame. This process passes on the benefits of the SR result to
the tracking module and allows the entire system to reach its
potential. We show results on a low-resolution facial video.
We demonstrate a significant improvement in face recognition rates with the super-resolved images over the images
without super-resolution.
Video-based face recognition has received significant attention in the past few years. However, the facial images
in a video sequence acquired from a distance are usually
small in size and their visual quality is low. Enhancing low-
resolution (LR) facial images from a video sequence is of
importance for performing face recognition. Registration is
a critical step in super-resolution (SR) of facial images from
a video which requires precise pose alignment and illumination normalization. Unlike traditional approaches that
perform tracking for each frame before using a SR method,
we present an incremental super-resolution
technique in which SR and tracking are linked together in
a closed-loop system. An incoming video frame is first registered in pose and normalized for illumination, and then
combined with the existing super-resolved texture. This
super-resolved texture, in turn, is used to improve the estimate of illumination and motion parameters for the next
frame. This process passes on the benefits of the SR result to
the tracking module and allows the entire system to reach its
potential. We show results on a low-resolution facial video.
We demonstrate a significant improvement in face recognition rates with the super-resolved images over the images
without super-resolution.
.png) A multilayered camera network architecture with nodes as entry/exit points, cameras, and clusters of cameras at different layers is proposed. This paper integrates face recognition that provides robustness to appearance changes and better models the time-varying traffic patterns in the network. The statistical dependence between the nodes, indicating the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, is represented by a weighted directed graph and transition times that may have multimodal distributions. The traffic patterns and the network topology may be changing in the dynamic environment. We propose a Monte Carlo Expectation-Maximization algorithm-based continuous learning mechanism to capture the latent dynamically changing characteristics of the network topology. In the experiments, a nine-camera network with twenty-five nodes (at the lowest level) is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments and compared with previous approaches.
A multilayered camera network architecture with nodes as entry/exit points, cameras, and clusters of cameras at different layers is proposed. This paper integrates face recognition that provides robustness to appearance changes and better models the time-varying traffic patterns in the network. The statistical dependence between the nodes, indicating the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, is represented by a weighted directed graph and transition times that may have multimodal distributions. The traffic patterns and the network topology may be changing in the dynamic environment. We propose a Monte Carlo Expectation-Maximization algorithm-based continuous learning mechanism to capture the latent dynamically changing characteristics of the network topology. In the experiments, a nine-camera network with twenty-five nodes (at the lowest level) is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments and compared with previous approaches.
 The widespread use of super-resolution methods, in a
variety of applications such as surveillance has led to
an increasing need for or quality assessment measures.
The current quality measures aim to compare different
fusion methods by assessing the quality of the fused images.
They consider the information transferred between
the super-resolved image and input images only. In this
paper, we propose an objective quality evaluation algorithm
for super-resolved images, which focuses on evaluating
the quality of super-resolved images that are constructed
from different conditions of input images. The
proposed quality evaluation method combines both the
relationship between the super-resolved image and the
input images, and the relationship between the input images.
Using the proposed measure, the quality of the
super-resolved face images constructed from videos are
evaluated under different conditions, including the variation
of pose, lighting, facial expressions and the number
of input images.
The widespread use of super-resolution methods, in a
variety of applications such as surveillance has led to
an increasing need for or quality assessment measures.
The current quality measures aim to compare different
fusion methods by assessing the quality of the fused images.
They consider the information transferred between
the super-resolved image and input images only. In this
paper, we propose an objective quality evaluation algorithm
for super-resolved images, which focuses on evaluating
the quality of super-resolved images that are constructed
from different conditions of input images. The
proposed quality evaluation method combines both the
relationship between the super-resolved image and the
input images, and the relationship between the input images.
Using the proposed measure, the quality of the
super-resolved face images constructed from videos are
evaluated under different conditions, including the variation
of pose, lighting, facial expressions and the number
of input images.
 Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR
algorithms for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to
the SR process. However, the registration is a challenging
task for SR with expression changes. This research proposes a
new method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution
(LR) facial image by handling the facial image in a nonrigid
manner. It consists of global tracking, local alignment
for precise registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline
based Resolution Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation
(RAIFFD) model is used to recover a dense local nonrigid
flow field. In this scheme, low-resolution image model
is explicitly embedded in the optimization function formulation
to simulate the formation of low resolution image.
The results achieved by the proposed approach are significantly
better as compared to the SR approaches applied
on the whole face image without considering local deformations.
The results are also compared with two state-ofthe-
art SR algorithms to show the effectiveness of the approach
in super-resolving facial images with local expression
changes.
Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR
algorithms for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to
the SR process. However, the registration is a challenging
task for SR with expression changes. This research proposes a
new method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution
(LR) facial image by handling the facial image in a nonrigid
manner. It consists of global tracking, local alignment
for precise registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline
based Resolution Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation
(RAIFFD) model is used to recover a dense local nonrigid
flow field. In this scheme, low-resolution image model
is explicitly embedded in the optimization function formulation
to simulate the formation of low resolution image.
The results achieved by the proposed approach are significantly
better as compared to the SR approaches applied
on the whole face image without considering local deformations.
The results are also compared with two state-ofthe-
art SR algorithms to show the effectiveness of the approach
in super-resolving facial images with local expression
changes.
 Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR algorithms
for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to the SR
process. However, the registration is a challenging task for
SR with expression changes. This research proposes a new
method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution (LR)
facial image by handling the facial image in a non-rigid manner.
It consists of global tracking, local alignment for precise
registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline based Resolution
Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation (RAIFFD) model
is used to recover a dense local non-rigid flow field. In this
scheme, low-resolution image model is explicitly embedded
in the optimization function formulation to simulate the formation
of low resolution image. The results achieved by the
proposed approach are significantly better as compared to
the SR approaches applied on the whole face image without
considering local deformations.
Super-resolution (SR) of facial images from video suffers
from facial expression changes. Most of the existing SR algorithms
for facial images make an unrealistic assumption
that the “perfect” registration has been done prior to the SR
process. However, the registration is a challenging task for
SR with expression changes. This research proposes a new
method for enhancing the resolution of low-resolution (LR)
facial image by handling the facial image in a non-rigid manner.
It consists of global tracking, local alignment for precise
registration and SR algorithms. A B-spline based Resolution
Aware Incremental Free Form Deformation (RAIFFD) model
is used to recover a dense local non-rigid flow field. In this
scheme, low-resolution image model is explicitly embedded
in the optimization function formulation to simulate the formation
of low resolution image. The results achieved by the
proposed approach are significantly better as compared to
the SR approaches applied on the whole face image without
considering local deformations.
 Video-based human recognition at a distance remains a challenging problem for the fusion of multimodal
biometrics. We present a
new approach that utilizes and integrates information from side face and gait at the feature level. The features of
face and gait are obtained separately using principal component analysis (PCA) from enhanced side face image
(ESFI) and gait energy image (GEI), respectively. Multiple discriminant analysis (MDA) is employed on the
concatenated features of face and gait to obtain discriminating synthetic features. The experimental results demonstrate that the synthetic features, encoding both side face and gait
information, carry more discriminating power than the individual biometrics features, and the proposed feature
level fusion scheme outperforms the match score level and another feature level fusion scheme.
Video-based human recognition at a distance remains a challenging problem for the fusion of multimodal
biometrics. We present a
new approach that utilizes and integrates information from side face and gait at the feature level. The features of
face and gait are obtained separately using principal component analysis (PCA) from enhanced side face image
(ESFI) and gait energy image (GEI), respectively. Multiple discriminant analysis (MDA) is employed on the
concatenated features of face and gait to obtain discriminating synthetic features. The experimental results demonstrate that the synthetic features, encoding both side face and gait
information, carry more discriminating power than the individual biometrics features, and the proposed feature
level fusion scheme outperforms the match score level and another feature level fusion scheme.
.png) This paper consider face, side face, gait and ear and their possible fusion for human recognition. It presents an overview of some of the techniques that we have developed for (a) super-resoulution-based face recognition in video, (b) gait-based recognition in video, (c) fusion of super-resolved side face and gait in video, (d) ear recognition in color/range images, and (e) fusion performance prediction and validation. It presents various real-world examples to illustrate the ideas and points out the relative merits of the approaches that are discussed.
This paper consider face, side face, gait and ear and their possible fusion for human recognition. It presents an overview of some of the techniques that we have developed for (a) super-resoulution-based face recognition in video, (b) gait-based recognition in video, (c) fusion of super-resolved side face and gait in video, (d) ear recognition in color/range images, and (e) fusion performance prediction and validation. It presents various real-world examples to illustrate the ideas and points out the relative merits of the approaches that are discussed.
 We have introduced a new video-based recognition method to recognize noncooperating individuals at a
distance in video who expose side views to the camera. Information from two biometrics sources, side face
and gait, is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, an enhanced side-face image (ESFI), a
higher resolution image compared with the image directly obtained from a single video frame, is constructed.
For gait, the gait energy image (GEI),
a spatiotemporal compact representation of gait in video, is used to characterize human-walking properties.
The experimental results show that the idea of constructing
ESFI from multiple frames is promising for human recognition in video, and better face features are extracted
from ESFI compared to those from the original side-face images (OSFIs).
We have introduced a new video-based recognition method to recognize noncooperating individuals at a
distance in video who expose side views to the camera. Information from two biometrics sources, side face
and gait, is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, an enhanced side-face image (ESFI), a
higher resolution image compared with the image directly obtained from a single video frame, is constructed.
For gait, the gait energy image (GEI),
a spatiotemporal compact representation of gait in video, is used to characterize human-walking properties.
The experimental results show that the idea of constructing
ESFI from multiple frames is promising for human recognition in video, and better face features are extracted
from ESFI compared to those from the original side-face images (OSFIs).
.png) Recently, ‘entry/exit’ events of objects in the field-of-views of cameras were used to learn the topology of the camera network. The integration of object appearance was also proposed to employ the visual information provided by the imaging sensors. A problem with these methods is the lack of robustness to appearance changes. This paper integrates face recognition in the statistical model to better estimate the correspondence in the time-varying network. The statistical dependence between the entry and exit nodes indicates the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, which are represented by a weighted directed graph and transition time distributions. A nine-camera network with 25 nodes is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments, and compared with the previous approaches.
Recently, ‘entry/exit’ events of objects in the field-of-views of cameras were used to learn the topology of the camera network. The integration of object appearance was also proposed to employ the visual information provided by the imaging sensors. A problem with these methods is the lack of robustness to appearance changes. This paper integrates face recognition in the statistical model to better estimate the correspondence in the time-varying network. The statistical dependence between the entry and exit nodes indicates the connectivity and traffic patterns of the camera network, which are represented by a weighted directed graph and transition time distributions. A nine-camera network with 25 nodes is analyzed both in simulation and in real-life experiments, and compared with the previous approaches.
.png) In this paper, we propose a method to incrementally superresolve 3D facial texture by integrating information frame by frame from a video captured under changing poses and illuminations. First, we recover illumination, 3D motion and shape parameters from our tracking algorithm. This information is then used to super-resolve 3D texture using Iterative BackProjection (IBP) method. Finally, the super-resolved texture is fed back to the tracking part to improve the estimation of illumination and motion parameters. This closed-loop process continues to refine the texture as new frames come in. We also propose a local-region based scheme to handle non-rigidity of the human face. Experiments demonstrate that our framework not only incrementally super-resolves facial images, but recovers the detailed expression changes in high quality.
In this paper, we propose a method to incrementally superresolve 3D facial texture by integrating information frame by frame from a video captured under changing poses and illuminations. First, we recover illumination, 3D motion and shape parameters from our tracking algorithm. This information is then used to super-resolve 3D texture using Iterative BackProjection (IBP) method. Finally, the super-resolved texture is fed back to the tracking part to improve the estimation of illumination and motion parameters. This closed-loop process continues to refine the texture as new frames come in. We also propose a local-region based scheme to handle non-rigidity of the human face. Experiments demonstrate that our framework not only incrementally super-resolves facial images, but recovers the detailed expression changes in high quality.
 We present a novel genetically
inspired learning method for facial expression recognition (FER). Our learning method can select visually meaningful
features automatically in a genetic programming-based approach that uses Gabor wavelet representation for
primitive features and linear/nonlinear operators to synthesize new features. To make use of random nature of a genetic
program, we design a multi-agent scheme to boost the performance. We compare the performance of our
approach with several approaches in the literature and show that our approach can perform the task of facial
expression recognition effectively.
We present a novel genetically
inspired learning method for facial expression recognition (FER). Our learning method can select visually meaningful
features automatically in a genetic programming-based approach that uses Gabor wavelet representation for
primitive features and linear/nonlinear operators to synthesize new features. To make use of random nature of a genetic
program, we design a multi-agent scheme to boost the performance. We compare the performance of our
approach with several approaches in the literature and show that our approach can perform the task of facial
expression recognition effectively.
 A new video based recognition method is presented
to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance in
video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait, is utilized
and integrated at feature level. For face, a high-resolution
side face image is constructed from multiple video frames.
For gait, Gait Energy Image (GEI), a spatio-temporal compact
representation of gait in video, is used to characterize
human walking properties. Face features and gait features
are obtained separately using Principal Component Analysis
(PCA) and Multiple Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined
method from the high-resolution side face image and
Gait Energy Image (GEI), respectively. The system is tested
on a database of video sequences corresponding to 46 people.
The results showed that the integrated face and gait
features carry the most discriminating power compared to
any individual biometric.
A new video based recognition method is presented
to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance in
video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait, is utilized
and integrated at feature level. For face, a high-resolution
side face image is constructed from multiple video frames.
For gait, Gait Energy Image (GEI), a spatio-temporal compact
representation of gait in video, is used to characterize
human walking properties. Face features and gait features
are obtained separately using Principal Component Analysis
(PCA) and Multiple Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined
method from the high-resolution side face image and
Gait Energy Image (GEI), respectively. The system is tested
on a database of video sequences corresponding to 46 people.
The results showed that the integrated face and gait
features carry the most discriminating power compared to
any individual biometric.
 Reconstruction-based super-resolution has been widely
treated in computer vision. However, super-resolution of
facial images has received very little attention. Since different
parts of a face may have different motions in normal
videos, we propose a new method for enhancing
the resolution of low-resolution facial image by handling
the facial image non-uniformly. We divide low-resolution
face image into different regions based on facial features
and estimate motions of each of these regions using different
motion models. Our experimental results show we can
achieve better results than applying super-resolution on the
whole face image uniformly.
Reconstruction-based super-resolution has been widely
treated in computer vision. However, super-resolution of
facial images has received very little attention. Since different
parts of a face may have different motions in normal
videos, we propose a new method for enhancing
the resolution of low-resolution facial image by handling
the facial image non-uniformly. We divide low-resolution
face image into different regions based on facial features
and estimate motions of each of these regions using different
motion models. Our experimental results show we can
achieve better results than applying super-resolution on the
whole face image uniformly.
 We introduce a new video based recognition
method to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance
in video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait,
is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, we
construct Enhanced Side Face Image (ESFI), a higher resolution
image compared with the image directly obtained
from a single video frame, to fuse information of face from
multiple video frames. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image
(GEI), a spatio-temporal compact representation of gait in
video, to characterize human walking properties. The features
of face and the features of gait are obtained separately
using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Multiple
Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined method from ESFI
and GEI, respectively. They are then integrated at match
score level. Our approach is tested on a database of video
sequences corresponding to 46 people. The different fusion
methods are compared and analyzed. The experimental results
show that (a) Integrated information from side face
and gait is effective for human recognition in video; (b) The
idea of constructing ESFI from multiple frames is promising
for human recognition in video and better face features are
extracted from ESFI compared to those from original face
images.
We introduce a new video based recognition
method to recognize non-cooperating individuals at a distance
in video, who expose side views to the camera. Information
from two biometric sources, side face and gait,
is utilized and integrated for recognition. For side face, we
construct Enhanced Side Face Image (ESFI), a higher resolution
image compared with the image directly obtained
from a single video frame, to fuse information of face from
multiple video frames. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image
(GEI), a spatio-temporal compact representation of gait in
video, to characterize human walking properties. The features
of face and the features of gait are obtained separately
using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Multiple
Discriminant Analysis (MDA) combined method from ESFI
and GEI, respectively. They are then integrated at match
score level. Our approach is tested on a database of video
sequences corresponding to 46 people. The different fusion
methods are compared and analyzed. The experimental results
show that (a) Integrated information from side face
and gait is effective for human recognition in video; (b) The
idea of constructing ESFI from multiple frames is promising
for human recognition in video and better face features are
extracted from ESFI compared to those from original face
images.
.png) Human recognition from arbitrary views is an important task for many applications, such as visual surveillance, covert security and access control. It has been found to be very difficult in reality, especially when a person is walking at a distance in read-world outdoor conditions. For optimal performance, the system should use as much information as possible from the observations. In this paper, we propose an innovative system, which combines cues of face profile and gait silhouette from the single camera video sequences. For optimal face profile recognition, we first reconstruct a high-resolution face profile image from several adjacent low-resolution video frames. Then we use a curvature-based matching method for recognition. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image (GEI) to characterize human walking properties. Recognition is carried out based on the direct GEI matching. Several schemes are considered for fusion of face profile and gait. A number of dynamic video sequences are tested to evaluate the performance of our system. Experiment results are compared and discussed.
Human recognition from arbitrary views is an important task for many applications, such as visual surveillance, covert security and access control. It has been found to be very difficult in reality, especially when a person is walking at a distance in read-world outdoor conditions. For optimal performance, the system should use as much information as possible from the observations. In this paper, we propose an innovative system, which combines cues of face profile and gait silhouette from the single camera video sequences. For optimal face profile recognition, we first reconstruct a high-resolution face profile image from several adjacent low-resolution video frames. Then we use a curvature-based matching method for recognition. For gait, we use Gait Energy Image (GEI) to characterize human walking properties. Recognition is carried out based on the direct GEI matching. Several schemes are considered for fusion of face profile and gait. A number of dynamic video sequences are tested to evaluate the performance of our system. Experiment results are compared and discussed.
 Face profile is an important aspect of face recognition and
it provides a complementary structure of the face that is
seen in the non-frontal view. In the past, several methods
have been proposed to recognize face profiles in still images.
However, face profile images that are captured at
a distance by surveillance cameras usually are video sequences
that have a low resolution. It is difficult to extract
accurate face profile directly from a low-resolution video
frame, which does not have many pixels on the face profile.
The emphasis of this research is to introduce a practical approach
for human recognition by using high-resolution face
profile images constructed from the low-resolution videos.
We use both the spatial and temporal information present
in a number of adjacent low-resolution frames of a video
sequence to construct high-resolution face profile images.
As the quality of high-resolution images relies on the correctness
of image alignment between consecutive frames,
an elastic registration algorithm is used for face profile image
alignment. A match statistic is designed to detect and
discard poorly aligned images which may degrade the quality
of the high-resolution face profile image. After obtaining
high-resolution face profile images, we use a dynamic time
warping method for face profile recognition. A number of
dynamic video sequences are tested to demonstrate the applicability
and reliability of our method.
Face profile is an important aspect of face recognition and
it provides a complementary structure of the face that is
seen in the non-frontal view. In the past, several methods
have been proposed to recognize face profiles in still images.
However, face profile images that are captured at
a distance by surveillance cameras usually are video sequences
that have a low resolution. It is difficult to extract
accurate face profile directly from a low-resolution video
frame, which does not have many pixels on the face profile.
The emphasis of this research is to introduce a practical approach
for human recognition by using high-resolution face
profile images constructed from the low-resolution videos.
We use both the spatial and temporal information present
in a number of adjacent low-resolution frames of a video
sequence to construct high-resolution face profile images.
As the quality of high-resolution images relies on the correctness
of image alignment between consecutive frames,
an elastic registration algorithm is used for face profile image
alignment. A match statistic is designed to detect and
discard poorly aligned images which may degrade the quality
of the high-resolution face profile image. After obtaining
high-resolution face profile images, we use a dynamic time
warping method for face profile recognition. A number of
dynamic video sequences are tested to demonstrate the applicability
and reliability of our method.
 Most of the current profile recognition algorithms
depend on the correct detection of fiducial points and the
determination of relationships among these fiducial
points. Unfortunately, some features such as concave
nose, protruding lips, flat chin, etc., make detection of
such points difficult and unreliable. Also, the number and
position of fiducial points vary when expression changes
even for the same person. A curvature based
matching approach is presented in this research, which does not
require the extraction of all the fiducial points, but uses
information contained in the profile. The scale space
filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the
curvature of the filtered profile is computed. Using the
curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple
method. Then a dynamic time warping method is applied
to match the face profile portion from nasion to throat
based on the curvature value. Experiments are performed
on two profile face image databases. Recognition rates
and conclusion are presented and discussed.
Most of the current profile recognition algorithms
depend on the correct detection of fiducial points and the
determination of relationships among these fiducial
points. Unfortunately, some features such as concave
nose, protruding lips, flat chin, etc., make detection of
such points difficult and unreliable. Also, the number and
position of fiducial points vary when expression changes
even for the same person. A curvature based
matching approach is presented in this research, which does not
require the extraction of all the fiducial points, but uses
information contained in the profile. The scale space
filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the
curvature of the filtered profile is computed. Using the
curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple
method. Then a dynamic time warping method is applied
to match the face profile portion from nasion to throat
based on the curvature value. Experiments are performed
on two profile face image databases. Recognition rates
and conclusion are presented and discussed.
 We present a curvature-based matching approach, which uses information contained in
the facial profile. The scale space filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the curvature of the
filtered profile is computed. Using the curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple method. Then a dynamic time warping method
is applied. Experiments are performed on two profile face image databases.
We present a curvature-based matching approach, which uses information contained in
the facial profile. The scale space filtering is used to smooth the profile and then the curvature of the
filtered profile is computed. Using the curvature value, the fiducial points, such as nasion and
throat can be reliably extracted using a fast and simple method. Then a dynamic time warping method
is applied. Experiments are performed on two profile face image databases.
 We introduce a novel genetically-inspired learning method for face expression recognition (FER) in visible images. Unlike
current research for FER that generally uses visually meaningful feature, we
proposed a Genetic Programming based technique, which learns to discover
composite operators and features that are evolved from combinations of
primitive image processing operations. In this approach, the output of the
learned composite operator is a feature vector that is used for FER. The
experimental results show that our approach can find good composite operators
to effectively extract useful features.
We introduce a novel genetically-inspired learning method for face expression recognition (FER) in visible images. Unlike
current research for FER that generally uses visually meaningful feature, we
proposed a Genetic Programming based technique, which learns to discover
composite operators and features that are evolved from combinations of
primitive image processing operations. In this approach, the output of the
learned composite operator is a feature vector that is used for FER. The
experimental results show that our approach can find good composite operators
to effectively extract useful features.