
|

|
Ev ve Ofis taşıma sektöründe lider olmak.Teknolojiyi klrd takip ederek bunu müşteri menuniyeti amacı için kullanmak.Sektörde marka olmak.
İstanbul evden eve nakliyat
Misyonumuz sayesinde edindiğimiz müşteri memnuniyeti ve güven ile müşterilerimizin bizi tavsiye etmelerini sağlamak.
Active Concept Learning in Image Databases
 We present
an active concept learning approach based on the mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a
database system: the changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we
a) propose a new user directed semi-supervised expectation-maximization
algorithm for mixture parameter estimation, and b) develop a novel model selection method based on
Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information.
Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our active concept
learning approach and the improvement in retrieval performance by concept transduction.
We present
an active concept learning approach based on the mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a
database system: the changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we
a) propose a new user directed semi-supervised expectation-maximization
algorithm for mixture parameter estimation, and b) develop a novel model selection method based on
Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information.
Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our active concept
learning approach and the improvement in retrieval performance by concept transduction.
On Labeling Noise and Outliers for Robust Concept Learning for Image Databases
 Recently mixture model has been used to model image databases. The retrieval experiences derived from multiple
users' relevance feedbacks have been used to improve model fitting in a semi-supervised manner.
However, the mixture model for image databases remains as a challenging task since the database may
contain clutter and outliers, and labelling information derived from multiple users may be inconsistent. Thus,
neither the mixture model nor the labelling information is as ideal as most of the researchers have previously
assumed. We (a) address the problems of the noise disturbances for both mixture model and
users' labelling information, (b) propose to process retrieval experiences in an intelligent manner using
Bayesian analysis, (c) present a robust mixture model fitting algorithm to achieve visual concept learning,
and (d) construct a concept-based indexing structure for efficient search of the database. The experimental
results on a Corel image set show the correctness of our retrieval experience analysis, the effectiveness of
the proposed concept learning approach, and the improvement of retrieval performance based on the
indexing structure.
Recently mixture model has been used to model image databases. The retrieval experiences derived from multiple
users' relevance feedbacks have been used to improve model fitting in a semi-supervised manner.
However, the mixture model for image databases remains as a challenging task since the database may
contain clutter and outliers, and labelling information derived from multiple users may be inconsistent. Thus,
neither the mixture model nor the labelling information is as ideal as most of the researchers have previously
assumed. We (a) address the problems of the noise disturbances for both mixture model and
users' labelling information, (b) propose to process retrieval experiences in an intelligent manner using
Bayesian analysis, (c) present a robust mixture model fitting algorithm to achieve visual concept learning,
and (d) construct a concept-based indexing structure for efficient search of the database. The experimental
results on a Corel image set show the correctness of our retrieval experience analysis, the effectiveness of
the proposed concept learning approach, and the improvement of retrieval performance based on the
indexing structure.
Active Concept Learning for Image Retrieval in Dynamic Databases
.png) Concept learning in content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems is a challenging task. This paper presents an active concept learning approach based on mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a database system: changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we develop a novel model selection method based on Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information. The analysis of exploitation vs. exploration in the search space helps to find optimal model efficiently. Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our approach.
Concept learning in content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems is a challenging task. This paper presents an active concept learning approach based on mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a database system: changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we develop a novel model selection method based on Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information. The analysis of exploitation vs. exploration in the search space helps to find optimal model efficiently. Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our approach.
Concept learning and transplantation for dynamic image databases
.png) The task of a content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system is to cater to users who ezpect to get relevant images with high precision and eficiency in response to query images. This paper presents a concept learning approach that integrates a mixture model of the data, relevance feedback and long-term continuous learning. The concepts are incrementally refined with increased retrieval ezperiences. The concept knowledge can be immediately tmnsplanted to deal with the dynamic database situations such as insertion of new images, removal of ensting images and query images which are outside the database. Experimental results on Core1 database show the eficacy of our approach.
The task of a content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system is to cater to users who ezpect to get relevant images with high precision and eficiency in response to query images. This paper presents a concept learning approach that integrates a mixture model of the data, relevance feedback and long-term continuous learning. The concepts are incrementally refined with increased retrieval ezperiences. The concept knowledge can be immediately tmnsplanted to deal with the dynamic database situations such as insertion of new images, removal of ensting images and query images which are outside the database. Experimental results on Core1 database show the eficacy of our approach.
Learning semantic visual concepts from video
.png) Increasing amounts of digital video data have become available with the rapid growth in video technology. As a result, there is a great need for automatic extraction of concepts or events of interest from video. In this paper, we present an approach for learning concepts from video. The approach consists of three steps. In the first step, video shot boundaries are detected, and from these shots keyframes are extracted, which are representatives of the shots. In the second step, key frames are segmented and a variety of features are computed In the third step, a classification by feature partitioning method is employed for learning different semantic concepts. The results are presented for successfully learning semantic concepts such as ocean, mountain, people, and building from a variety of digital videos.
Increasing amounts of digital video data have become available with the rapid growth in video technology. As a result, there is a great need for automatic extraction of concepts or events of interest from video. In this paper, we present an approach for learning concepts from video. The approach consists of three steps. In the first step, video shot boundaries are detected, and from these shots keyframes are extracted, which are representatives of the shots. In the second step, key frames are segmented and a variety of features are computed In the third step, a classification by feature partitioning method is employed for learning different semantic concepts. The results are presented for successfully learning semantic concepts such as ocean, mountain, people, and building from a variety of digital videos.
Concept learning with fuzzy clustering and relevance feedback
.png) In recent years feedback approaches have been used in relating low-level image features with concepts to overcome the subjective nature of the human image interpretation. Generally, in these systems when the user starts with a new query, the entire prior experience of the system is lost. In this paper, we address the problem of incorporating prior experience of the retrieval system to improve the performance on future queries. We propose a semi-supervised fuzzyclustering method to learn class distribution (meta knowledge) in the sense of high-level concepts from retrieval experience. Using fuzzyrules, we incorporate the meta knowledge into a probabilistic feature relevance feedback approach to improve the retrieval performance. Results on synthetic and real databases show that our approach provides better retrieval precision compared to the case when no retrieval experience is used.
In recent years feedback approaches have been used in relating low-level image features with concepts to overcome the subjective nature of the human image interpretation. Generally, in these systems when the user starts with a new query, the entire prior experience of the system is lost. In this paper, we address the problem of incorporating prior experience of the retrieval system to improve the performance on future queries. We propose a semi-supervised fuzzyclustering method to learn class distribution (meta knowledge) in the sense of high-level concepts from retrieval experience. Using fuzzyrules, we incorporate the meta knowledge into a probabilistic feature relevance feedback approach to improve the retrieval performance. Results on synthetic and real databases show that our approach provides better retrieval precision compared to the case when no retrieval experience is used.
Learned templates for feature extraction in fingerprint images
.png) Most current techniques for minutiae extraction in fingerprint images utilize complex preprocessing and postprocessing. In this paper, we propose a new technique, based on the use of learned templates, which statistically characterize the minutiae. Templates are learned from examples by optimizing a criterion function using Lagrange's method. To detect the presence of minutiae in test images, templates are applied with appropriate orientations to the binary image only at selected potential minutia locations. Several performance measures, which evaluate the quality and quantity of extracted features and their impact on identification, are used to evaluate the signi3cance of learned templates. The performance of the proposed approach is evaluated on two sets of fingerprint images: one is collected by an optical scanner and the other one is chosen from NIST special fingerprint database 4. The experimental results show that learned templates can improve both the features and the performance of the identification system.
Most current techniques for minutiae extraction in fingerprint images utilize complex preprocessing and postprocessing. In this paper, we propose a new technique, based on the use of learned templates, which statistically characterize the minutiae. Templates are learned from examples by optimizing a criterion function using Lagrange's method. To detect the presence of minutiae in test images, templates are applied with appropriate orientations to the binary image only at selected potential minutia locations. Several performance measures, which evaluate the quality and quantity of extracted features and their impact on identification, are used to evaluate the signi3cance of learned templates. The performance of the proposed approach is evaluated on two sets of fingerprint images: one is collected by an optical scanner and the other one is chosen from NIST special fingerprint database 4. The experimental results show that learned templates can improve both the features and the performance of the identification system.
Exploitation of meta knowledge for learning visual concepts
.png) The paper proposes a content-based image retrieval system which can learn visual concepts and refine them incrementally with increased retrieval experiences captured over time. The approach consists of using fuzzy clustering for learning concepts in conjunction with statistical learning for computing "relevance" weights of features used to represent images in the database. As the clusters become relatively stable and correspond to human concept distribution, the system can yield fast retrievals with higher precision. The paper presents a discussion on problems such as the system mistakenly indentifying a concept, a large number of trials to achieve clustering, etc. Experiments on synthetic data and real image database demonstrate the efficacy of this approach.
The paper proposes a content-based image retrieval system which can learn visual concepts and refine them incrementally with increased retrieval experiences captured over time. The approach consists of using fuzzy clustering for learning concepts in conjunction with statistical learning for computing "relevance" weights of features used to represent images in the database. As the clusters become relatively stable and correspond to human concept distribution, the system can yield fast retrievals with higher precision. The paper presents a discussion on problems such as the system mistakenly indentifying a concept, a large number of trials to achieve clustering, etc. Experiments on synthetic data and real image database demonstrate the efficacy of this approach.
Validation of SAR ATR performance predictions using learned distortion models
.png) Performance prediction of SAR ATR has been a challenging problem. In our previous work, we developed a statistical framework for predicting bounds on fundamental performance of vote-based SAR ATR using scattering centers. This framework considered data distortion factors such as uncertainty, occlusion and clutter, in addition to model similarity. In this paper, we present an initial study on learning the statistical distributions of these factors. We focus on the development of a method for learning the distribution of a parameter that encodes the combined eect of the occlusion and similarity factors on performance. The impact of incorporating such a distribution on the accuracy of the predicted bounds is demonstrated by comparing bounds obtained using it with those obtained assuming simplied distributions. The data used in the experiments are obtained from the MSTAR public domain under dierent congurations and depression angles. Keywords: Model-based SAR ATR, performance prediction and validation, learned distortion models, MSTAR data 1.
Performance prediction of SAR ATR has been a challenging problem. In our previous work, we developed a statistical framework for predicting bounds on fundamental performance of vote-based SAR ATR using scattering centers. This framework considered data distortion factors such as uncertainty, occlusion and clutter, in addition to model similarity. In this paper, we present an initial study on learning the statistical distributions of these factors. We focus on the development of a method for learning the distribution of a parameter that encodes the combined eect of the occlusion and similarity factors on performance. The impact of incorporating such a distribution on the accuracy of the predicted bounds is demonstrated by comparing bounds obtained using it with those obtained assuming simplied distributions. The data used in the experiments are obtained from the MSTAR public domain under dierent congurations and depression angles. Keywords: Model-based SAR ATR, performance prediction and validation, learned distortion models, MSTAR data 1.
Local Discriminative Learning for Pattern Recognition
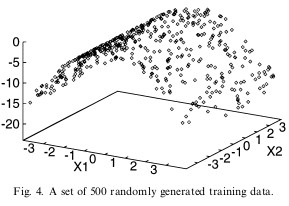 Local discriminative learning methods approximate a target function
directly by partitioning the feature space into a set of local regions, and appropriately modeling a simple
input-output relationship (function) in each one. We present a new method for judiciously partitioning
the input feature space in order to accurately represent the target function. The method accomplishes this by
approximating not only the target function itself but also its derivatives. As such, the method partitions the input
feature space along those dimensions for which the class probability function changes most rapidly, thus
minimizing bias. The efficacy of the method is validated using a variety of simulated and real-world data.
Local discriminative learning methods approximate a target function
directly by partitioning the feature space into a set of local regions, and appropriately modeling a simple
input-output relationship (function) in each one. We present a new method for judiciously partitioning
the input feature space in order to accurately represent the target function. The method accomplishes this by
approximating not only the target function itself but also its derivatives. As such, the method partitions the input
feature space along those dimensions for which the class probability function changes most rapidly, thus
minimizing bias. The efficacy of the method is validated using a variety of simulated and real-world data.
Oracle: An Integrated Learning Approach for Object Recognition
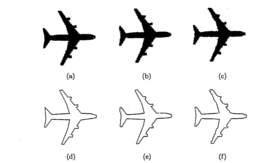 Model-based object recognition had become a popular paradigm in computer vision research and in most of the model-based vision systems, the object models used for recognition were generally a priori given (e.g. obtained using a CAD model). For many object recognition applications , it was not realistic to utilize a fixed object model database with static model features, but it was desirable to have a recognition system capable of performing automated object model acquisition and refinement. In order to achieve these capabilities, we developed a system called ORACLE (Object Recognition Accomplished through Consolidated Learning Expertise) that used two machine learning techniques known as Explanation-Based Learning (EBL) and Structured Conceptual Clustering (SCC) combined in a synergistic manner. As compared to systems which learned from numerous positive and negative examples, EBL allowed the generalization of object model descriptions from a single example and then constructed an efficient classification tree which was incrementally built and modified over time. Learning from experience was used to dynamically update the specific feature values of each object. These capabilities provided a dynamic object model database which allowed the system to exhibit improved performance over time.
Model-based object recognition had become a popular paradigm in computer vision research and in most of the model-based vision systems, the object models used for recognition were generally a priori given (e.g. obtained using a CAD model). For many object recognition applications , it was not realistic to utilize a fixed object model database with static model features, but it was desirable to have a recognition system capable of performing automated object model acquisition and refinement. In order to achieve these capabilities, we developed a system called ORACLE (Object Recognition Accomplished through Consolidated Learning Expertise) that used two machine learning techniques known as Explanation-Based Learning (EBL) and Structured Conceptual Clustering (SCC) combined in a synergistic manner. As compared to systems which learned from numerous positive and negative examples, EBL allowed the generalization of object model descriptions from a single example and then constructed an efficient classification tree which was incrementally built and modified over time. Learning from experience was used to dynamically update the specific feature values of each object. These capabilities provided a dynamic object model database which allowed the system to exhibit improved performance over time.
|
|


 We present
an active concept learning approach based on the mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a
database system: the changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we
a) propose a new user directed semi-supervised expectation-maximization
algorithm for mixture parameter estimation, and b) develop a novel model selection method based on
Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information.
Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our active concept
learning approach and the improvement in retrieval performance by concept transduction.
We present
an active concept learning approach based on the mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a
database system: the changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we
a) propose a new user directed semi-supervised expectation-maximization
algorithm for mixture parameter estimation, and b) develop a novel model selection method based on
Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information.
Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our active concept
learning approach and the improvement in retrieval performance by concept transduction.
 Recently mixture model has been used to model image databases. The retrieval experiences derived from multiple
users' relevance feedbacks have been used to improve model fitting in a semi-supervised manner.
However, the mixture model for image databases remains as a challenging task since the database may
contain clutter and outliers, and labelling information derived from multiple users may be inconsistent. Thus,
neither the mixture model nor the labelling information is as ideal as most of the researchers have previously
assumed. We (a) address the problems of the noise disturbances for both mixture model and
users' labelling information, (b) propose to process retrieval experiences in an intelligent manner using
Bayesian analysis, (c) present a robust mixture model fitting algorithm to achieve visual concept learning,
and (d) construct a concept-based indexing structure for efficient search of the database. The experimental
results on a Corel image set show the correctness of our retrieval experience analysis, the effectiveness of
the proposed concept learning approach, and the improvement of retrieval performance based on the
indexing structure.
Recently mixture model has been used to model image databases. The retrieval experiences derived from multiple
users' relevance feedbacks have been used to improve model fitting in a semi-supervised manner.
However, the mixture model for image databases remains as a challenging task since the database may
contain clutter and outliers, and labelling information derived from multiple users may be inconsistent. Thus,
neither the mixture model nor the labelling information is as ideal as most of the researchers have previously
assumed. We (a) address the problems of the noise disturbances for both mixture model and
users' labelling information, (b) propose to process retrieval experiences in an intelligent manner using
Bayesian analysis, (c) present a robust mixture model fitting algorithm to achieve visual concept learning,
and (d) construct a concept-based indexing structure for efficient search of the database. The experimental
results on a Corel image set show the correctness of our retrieval experience analysis, the effectiveness of
the proposed concept learning approach, and the improvement of retrieval performance based on the
indexing structure.
.png) Concept learning in content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems is a challenging task. This paper presents an active concept learning approach based on mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a database system: changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we develop a novel model selection method based on Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information. The analysis of exploitation vs. exploration in the search space helps to find optimal model efficiently. Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our approach.
Concept learning in content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems is a challenging task. This paper presents an active concept learning approach based on mixture model to deal with the two basic aspects of a database system: changing (image insertion or removal) nature of a database and user queries. To achieve concept learning, we develop a novel model selection method based on Bayesian analysis that evaluates the consistency of hypothesized models with the available information. The analysis of exploitation vs. exploration in the search space helps to find optimal model efficiently. Experimental results on Corel database show the efficacy of our approach.
.png) The task of a content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system is to cater to users who ezpect to get relevant images with high precision and eficiency in response to query images. This paper presents a concept learning approach that integrates a mixture model of the data, relevance feedback and long-term continuous learning. The concepts are incrementally refined with increased retrieval ezperiences. The concept knowledge can be immediately tmnsplanted to deal with the dynamic database situations such as insertion of new images, removal of ensting images and query images which are outside the database. Experimental results on Core1 database show the eficacy of our approach.
The task of a content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system is to cater to users who ezpect to get relevant images with high precision and eficiency in response to query images. This paper presents a concept learning approach that integrates a mixture model of the data, relevance feedback and long-term continuous learning. The concepts are incrementally refined with increased retrieval ezperiences. The concept knowledge can be immediately tmnsplanted to deal with the dynamic database situations such as insertion of new images, removal of ensting images and query images which are outside the database. Experimental results on Core1 database show the eficacy of our approach.
.png) Increasing amounts of digital video data have become available with the rapid growth in video technology. As a result, there is a great need for automatic extraction of concepts or events of interest from video. In this paper, we present an approach for learning concepts from video. The approach consists of three steps. In the first step, video shot boundaries are detected, and from these shots keyframes are extracted, which are representatives of the shots. In the second step, key frames are segmented and a variety of features are computed In the third step, a classification by feature partitioning method is employed for learning different semantic concepts. The results are presented for successfully learning semantic concepts such as ocean, mountain, people, and building from a variety of digital videos.
Increasing amounts of digital video data have become available with the rapid growth in video technology. As a result, there is a great need for automatic extraction of concepts or events of interest from video. In this paper, we present an approach for learning concepts from video. The approach consists of three steps. In the first step, video shot boundaries are detected, and from these shots keyframes are extracted, which are representatives of the shots. In the second step, key frames are segmented and a variety of features are computed In the third step, a classification by feature partitioning method is employed for learning different semantic concepts. The results are presented for successfully learning semantic concepts such as ocean, mountain, people, and building from a variety of digital videos.
.png) In recent years feedback approaches have been used in relating low-level image features with concepts to overcome the subjective nature of the human image interpretation. Generally, in these systems when the user starts with a new query, the entire prior experience of the system is lost. In this paper, we address the problem of incorporating prior experience of the retrieval system to improve the performance on future queries. We propose a semi-supervised fuzzyclustering method to learn class distribution (meta knowledge) in the sense of high-level concepts from retrieval experience. Using fuzzyrules, we incorporate the meta knowledge into a probabilistic feature relevance feedback approach to improve the retrieval performance. Results on synthetic and real databases show that our approach provides better retrieval precision compared to the case when no retrieval experience is used.
In recent years feedback approaches have been used in relating low-level image features with concepts to overcome the subjective nature of the human image interpretation. Generally, in these systems when the user starts with a new query, the entire prior experience of the system is lost. In this paper, we address the problem of incorporating prior experience of the retrieval system to improve the performance on future queries. We propose a semi-supervised fuzzyclustering method to learn class distribution (meta knowledge) in the sense of high-level concepts from retrieval experience. Using fuzzyrules, we incorporate the meta knowledge into a probabilistic feature relevance feedback approach to improve the retrieval performance. Results on synthetic and real databases show that our approach provides better retrieval precision compared to the case when no retrieval experience is used.
.png) Most current techniques for minutiae extraction in fingerprint images utilize complex preprocessing and postprocessing. In this paper, we propose a new technique, based on the use of learned templates, which statistically characterize the minutiae. Templates are learned from examples by optimizing a criterion function using Lagrange's method. To detect the presence of minutiae in test images, templates are applied with appropriate orientations to the binary image only at selected potential minutia locations. Several performance measures, which evaluate the quality and quantity of extracted features and their impact on identification, are used to evaluate the signi3cance of learned templates. The performance of the proposed approach is evaluated on two sets of fingerprint images: one is collected by an optical scanner and the other one is chosen from NIST special fingerprint database 4. The experimental results show that learned templates can improve both the features and the performance of the identification system.
Most current techniques for minutiae extraction in fingerprint images utilize complex preprocessing and postprocessing. In this paper, we propose a new technique, based on the use of learned templates, which statistically characterize the minutiae. Templates are learned from examples by optimizing a criterion function using Lagrange's method. To detect the presence of minutiae in test images, templates are applied with appropriate orientations to the binary image only at selected potential minutia locations. Several performance measures, which evaluate the quality and quantity of extracted features and their impact on identification, are used to evaluate the signi3cance of learned templates. The performance of the proposed approach is evaluated on two sets of fingerprint images: one is collected by an optical scanner and the other one is chosen from NIST special fingerprint database 4. The experimental results show that learned templates can improve both the features and the performance of the identification system.
.png) The paper proposes a content-based image retrieval system which can learn visual concepts and refine them incrementally with increased retrieval experiences captured over time. The approach consists of using fuzzy clustering for learning concepts in conjunction with statistical learning for computing "relevance" weights of features used to represent images in the database. As the clusters become relatively stable and correspond to human concept distribution, the system can yield fast retrievals with higher precision. The paper presents a discussion on problems such as the system mistakenly indentifying a concept, a large number of trials to achieve clustering, etc. Experiments on synthetic data and real image database demonstrate the efficacy of this approach.
The paper proposes a content-based image retrieval system which can learn visual concepts and refine them incrementally with increased retrieval experiences captured over time. The approach consists of using fuzzy clustering for learning concepts in conjunction with statistical learning for computing "relevance" weights of features used to represent images in the database. As the clusters become relatively stable and correspond to human concept distribution, the system can yield fast retrievals with higher precision. The paper presents a discussion on problems such as the system mistakenly indentifying a concept, a large number of trials to achieve clustering, etc. Experiments on synthetic data and real image database demonstrate the efficacy of this approach.
.png) Performance prediction of SAR ATR has been a challenging problem. In our previous work, we developed a statistical framework for predicting bounds on fundamental performance of vote-based SAR ATR using scattering centers. This framework considered data distortion factors such as uncertainty, occlusion and clutter, in addition to model similarity. In this paper, we present an initial study on learning the statistical distributions of these factors. We focus on the development of a method for learning the distribution of a parameter that encodes the combined eect of the occlusion and similarity factors on performance. The impact of incorporating such a distribution on the accuracy of the predicted bounds is demonstrated by comparing bounds obtained using it with those obtained assuming simplied distributions. The data used in the experiments are obtained from the MSTAR public domain under dierent congurations and depression angles. Keywords: Model-based SAR ATR, performance prediction and validation, learned distortion models, MSTAR data 1.
Performance prediction of SAR ATR has been a challenging problem. In our previous work, we developed a statistical framework for predicting bounds on fundamental performance of vote-based SAR ATR using scattering centers. This framework considered data distortion factors such as uncertainty, occlusion and clutter, in addition to model similarity. In this paper, we present an initial study on learning the statistical distributions of these factors. We focus on the development of a method for learning the distribution of a parameter that encodes the combined eect of the occlusion and similarity factors on performance. The impact of incorporating such a distribution on the accuracy of the predicted bounds is demonstrated by comparing bounds obtained using it with those obtained assuming simplied distributions. The data used in the experiments are obtained from the MSTAR public domain under dierent congurations and depression angles. Keywords: Model-based SAR ATR, performance prediction and validation, learned distortion models, MSTAR data 1.
 Local discriminative learning methods approximate a target function
directly by partitioning the feature space into a set of local regions, and appropriately modeling a simple
input-output relationship (function) in each one. We present a new method for judiciously partitioning
the input feature space in order to accurately represent the target function. The method accomplishes this by
approximating not only the target function itself but also its derivatives. As such, the method partitions the input
feature space along those dimensions for which the class probability function changes most rapidly, thus
minimizing bias. The efficacy of the method is validated using a variety of simulated and real-world data.
Local discriminative learning methods approximate a target function
directly by partitioning the feature space into a set of local regions, and appropriately modeling a simple
input-output relationship (function) in each one. We present a new method for judiciously partitioning
the input feature space in order to accurately represent the target function. The method accomplishes this by
approximating not only the target function itself but also its derivatives. As such, the method partitions the input
feature space along those dimensions for which the class probability function changes most rapidly, thus
minimizing bias. The efficacy of the method is validated using a variety of simulated and real-world data.
 Model-based object recognition had become a popular paradigm in computer vision research and in most of the model-based vision systems, the object models used for recognition were generally a priori given (e.g. obtained using a CAD model). For many object recognition applications , it was not realistic to utilize a fixed object model database with static model features, but it was desirable to have a recognition system capable of performing automated object model acquisition and refinement. In order to achieve these capabilities, we developed a system called ORACLE (Object Recognition Accomplished through Consolidated Learning Expertise) that used two machine learning techniques known as Explanation-Based Learning (EBL) and Structured Conceptual Clustering (SCC) combined in a synergistic manner. As compared to systems which learned from numerous positive and negative examples, EBL allowed the generalization of object model descriptions from a single example and then constructed an efficient classification tree which was incrementally built and modified over time. Learning from experience was used to dynamically update the specific feature values of each object. These capabilities provided a dynamic object model database which allowed the system to exhibit improved performance over time.
Model-based object recognition had become a popular paradigm in computer vision research and in most of the model-based vision systems, the object models used for recognition were generally a priori given (e.g. obtained using a CAD model). For many object recognition applications , it was not realistic to utilize a fixed object model database with static model features, but it was desirable to have a recognition system capable of performing automated object model acquisition and refinement. In order to achieve these capabilities, we developed a system called ORACLE (Object Recognition Accomplished through Consolidated Learning Expertise) that used two machine learning techniques known as Explanation-Based Learning (EBL) and Structured Conceptual Clustering (SCC) combined in a synergistic manner. As compared to systems which learned from numerous positive and negative examples, EBL allowed the generalization of object model descriptions from a single example and then constructed an efficient classification tree which was incrementally built and modified over time. Learning from experience was used to dynamically update the specific feature values of each object. These capabilities provided a dynamic object model database which allowed the system to exhibit improved performance over time.