
|

|
Ev ve Ofis taşıma sektöründe lider olmak.Teknolojiyi klrd takip ederek bunu müşteri menuniyeti amacı için kullanmak.Sektörde marka olmak.
İstanbul evden eve nakliyat
Misyonumuz sayesinde edindiğimiz müşteri memnuniyeti ve güven ile müşterilerimizin bizi tavsiye etmelerini sağlamak.
Context guided belief propagation for remote sensing image classification
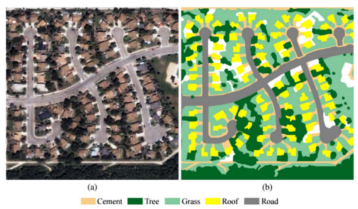 Proposed is a context guided belief propagation (BP) algorithm to perform high spatial resolution multispectral imagery (HSRMI) classification efficiently utilizing superpixel representation. One important characteristic of HSRMI is that different land cover objects possess a similar spectral property that is exploited to speed up the standard BP (SBP) in the classification process. Specifically, we leverage this property of HSRMI as context information to guide messages passing in SBP. Furthermore, the spectral and structural features extracted at the superpixel level are fed into a Markov random field framework to address the challenge of low interclass variation in HSRMI classification by minimizing the discrete energy through context guided BP (CBP).
Proposed is a context guided belief propagation (BP) algorithm to perform high spatial resolution multispectral imagery (HSRMI) classification efficiently utilizing superpixel representation. One important characteristic of HSRMI is that different land cover objects possess a similar spectral property that is exploited to speed up the standard BP (SBP) in the classification process. Specifically, we leverage this property of HSRMI as context information to guide messages passing in SBP. Furthermore, the spectral and structural features extracted at the superpixel level are fed into a Markov random field framework to address the challenge of low interclass variation in HSRMI classification by minimizing the discrete energy through context guided BP (CBP).
Visual and Contextual Modeling for the Detection of Repeated m-TBI
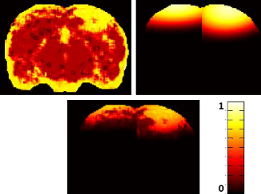 Currently, there is a lack of computational methods for the evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury
(mTBI). Further, the development of automated analyses has
been hindered by the subtle nature of mTBI abnormalities.
We present an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context
and low-level visual information. The visual model utilizes
texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine.
Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and
patients by improving clinical care.
Currently, there is a lack of computational methods for the evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury
(mTBI). Further, the development of automated analyses has
been hindered by the subtle nature of mTBI abnormalities.
We present an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context
and low-level visual information. The visual model utilizes
texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine.
Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and
patients by improving clinical care.
Dynamic Low-Level Context for the Detection of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
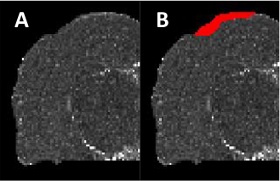 Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) appears as low contrast lesions in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
Standard automated detection approaches cannot detect the subtle changes caused by the lesions.
We've proposed and integrated new context features to improve the detection of mTBI lesions.
The approach is validated on a temporal mTBI rat model dataset and shown to have improved dice score and
convergence compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) appears as low contrast lesions in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
Standard automated detection approaches cannot detect the subtle changes caused by the lesions.
We've proposed and integrated new context features to improve the detection of mTBI lesions.
The approach is validated on a temporal mTBI rat model dataset and shown to have improved dice score and
convergence compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
A New Multi-scale Fuzzy Model for Histogram-based Descriptors
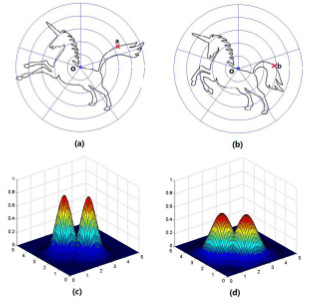 We present a general Multi-Scale Fuzzy
Model (MSFM) which handles distortions at different scales
in Histogram-Based Descriptors(HBDs). This model
can be applied both on one-dimensional HBDs and multidimensional
HBDs. We then focus on applying MSFM on
the widely used Shape Context for a Simplified Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (SMFSC) descriptor. Fuzzy models are
barely used in multi-dimensional HBDs due to the significant
increase of computational complexity. We show that by introducing
an intra-bin point location approximation and an approximate
iterative fuzzification approach, the algorithm can
be simplified and thus SMFSC hardly increases computational
complexity. Experiments on standard shape dataset show
that SMFSC improves upon the Inner Distance Shape Context.
We also applied SMFSC on Content-Based Product Image
Retrieval and the experimental results further validate the
effectiveness of our model.
We present a general Multi-Scale Fuzzy
Model (MSFM) which handles distortions at different scales
in Histogram-Based Descriptors(HBDs). This model
can be applied both on one-dimensional HBDs and multidimensional
HBDs. We then focus on applying MSFM on
the widely used Shape Context for a Simplified Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (SMFSC) descriptor. Fuzzy models are
barely used in multi-dimensional HBDs due to the significant
increase of computational complexity. We show that by introducing
an intra-bin point location approximation and an approximate
iterative fuzzification approach, the algorithm can
be simplified and thus SMFSC hardly increases computational
complexity. Experiments on standard shape dataset show
that SMFSC improves upon the Inner Distance Shape Context.
We also applied SMFSC on Content-Based Product Image
Retrieval and the experimental results further validate the
effectiveness of our model.
MFSC: A New Shape Descriptor with Robustness to Deformations
 We propose a new shape descriptor, Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (MFSC), which is highlighted by its robustness to
deformations. A novel multi-scale fuzzy model is presented
and applied on the widely used shape descriptor Shape Context
to generate MFSC. The multi-scale fuzzy model can handle
shape deformations of different scales, which makes MFSC
robust to various deformations. Experiments on an articulated
shape dataset demonstrate performance improvement
gained by MFSC over existing methods. We also applied
MFSC on a real-world application, Content-Based Product
Image Retrieval, and the experimental results further validate
its effectiveness. We make our code and experimental data
publicly available for future reference.
We propose a new shape descriptor, Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (MFSC), which is highlighted by its robustness to
deformations. A novel multi-scale fuzzy model is presented
and applied on the widely used shape descriptor Shape Context
to generate MFSC. The multi-scale fuzzy model can handle
shape deformations of different scales, which makes MFSC
robust to various deformations. Experiments on an articulated
shape dataset demonstrate performance improvement
gained by MFSC over existing methods. We also applied
MFSC on a real-world application, Content-Based Product
Image Retrieval, and the experimental results further validate
its effectiveness. We make our code and experimental data
publicly available for future reference.
Mild traumatic brain injury detection through visual and contextual modeling
.png) This paper proposes an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context and low-level visual information. The contextual model estimates the progression of the disease using subject information, such as the time since injury and the knowledge about the location of mTBI. The visual model utilizes texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine to maximize the discrimination in unimodal MR images. These two models are fused to obtain a final estimate of the locations of the mTBI lesion. The models are tested using a novel rodent model of repeated mTBI dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the fusion of both contextual and visual textural features outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches. Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and patients by improving clinical care.
This paper proposes an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context and low-level visual information. The contextual model estimates the progression of the disease using subject information, such as the time since injury and the knowledge about the location of mTBI. The visual model utilizes texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine to maximize the discrimination in unimodal MR images. These two models are fused to obtain a final estimate of the locations of the mTBI lesion. The models are tested using a novel rodent model of repeated mTBI dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the fusion of both contextual and visual textural features outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches. Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and patients by improving clinical care.
Gait recognition by combining classifiers based on environmental contexts
.png) Human gait properties can be affected by various environmental contexts such as walking surface and carrying objects. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for individual recognition by combining different gait classifiers with the knowledge of environmental contexts to improve the recognition performance. Different classifiers are designed to handle different environmental contexts, and context specific features are explored for context characterization. In the recognition procedure, we can determine the probability of environmental contexts in any probe sequence according to its context features, and apply the probabilistic classifier combination strategies for the recognition. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Human gait properties can be affected by various environmental contexts such as walking surface and carrying objects. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for individual recognition by combining different gait classifiers with the knowledge of environmental contexts to improve the recognition performance. Different classifiers are designed to handle different environmental contexts, and context specific features are explored for context characterization. In the recognition procedure, we can determine the probability of environmental contexts in any probe sequence according to its context features, and apply the probabilistic classifier combination strategies for the recognition. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
|
|
Top Slot Gacor Online Populer Paling Banyak di Mainkan 2025-2026 di Indonesia
Slot Toto Togel Gacor
Join toto togel Paling Banyak Di mainkan.
Situs Toto
With situs toto, mainkan game kesukaanmu di sini.
best online gambling rupiahtoto
rupiahtotorupiahtoto deposit sekali wd berkali-kali.
platform terbaik toto slot online
rupiahtoto raih kemenanganmu di rupiahtoto.
rupiahtoto : pusatnya slot togel online populer
ingat hanya di rupiahtoto rupiahtoto deposit 10rb WD sultan.
slot dengan pembayaran lengkap
slot ovoslot ovo, plat and win.
rupiahtoto best slot togel in Indonesia
Sign up at rupiahtoto situs resmi sejuta umat, menang dengan mudah di sini!.
toto slot terupdate dengan RTP tinggi
toto slot toto slot terbanyak di mainkan sepanjang masa.
slot dana deposit murah
Find success at slot dana agen slot dana dengan metode-metode depo gampang
sweet bonanza terbaik
Enjoy live betting like never before at sweet bonanzagame slot sweet bonanza tergacor saat ini.
link situs terbaik di Indonesia dalam permainan judi online resmi
amazing slot togel onlinerupiahtoto pasang angka impian mu di sini.
slot gacor: nomor #1 di Indonesia
slot gacorslot gacorbest slot gacor Indonesia.
https://amps303.org/
https://amps303.org/ https://amps303.org/https://amps303.org/


 Currently, there is a lack of computational methods for the evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury
(mTBI). Further, the development of automated analyses has
been hindered by the subtle nature of mTBI abnormalities.
We present an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context
and low-level visual information. The visual model utilizes
texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine.
Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and
patients by improving clinical care.
Currently, there is a lack of computational methods for the evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury
(mTBI). Further, the development of automated analyses has
been hindered by the subtle nature of mTBI abnormalities.
We present an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context
and low-level visual information. The visual model utilizes
texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine.
Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and
patients by improving clinical care.
 Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) appears as low contrast lesions in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
Standard automated detection approaches cannot detect the subtle changes caused by the lesions.
We've proposed and integrated new context features to improve the detection of mTBI lesions.
The approach is validated on a temporal mTBI rat model dataset and shown to have improved dice score and
convergence compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) appears as low contrast lesions in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
Standard automated detection approaches cannot detect the subtle changes caused by the lesions.
We've proposed and integrated new context features to improve the detection of mTBI lesions.
The approach is validated on a temporal mTBI rat model dataset and shown to have improved dice score and
convergence compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
 We present a general Multi-Scale Fuzzy
Model (MSFM) which handles distortions at different scales
in Histogram-Based Descriptors(HBDs). This model
can be applied both on one-dimensional HBDs and multidimensional
HBDs. We then focus on applying MSFM on
the widely used Shape Context for a Simplified Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (SMFSC) descriptor. Fuzzy models are
barely used in multi-dimensional HBDs due to the significant
increase of computational complexity. We show that by introducing
an intra-bin point location approximation and an approximate
iterative fuzzification approach, the algorithm can
be simplified and thus SMFSC hardly increases computational
complexity. Experiments on standard shape dataset show
that SMFSC improves upon the Inner Distance Shape Context.
We also applied SMFSC on Content-Based Product Image
Retrieval and the experimental results further validate the
effectiveness of our model.
We present a general Multi-Scale Fuzzy
Model (MSFM) which handles distortions at different scales
in Histogram-Based Descriptors(HBDs). This model
can be applied both on one-dimensional HBDs and multidimensional
HBDs. We then focus on applying MSFM on
the widely used Shape Context for a Simplified Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (SMFSC) descriptor. Fuzzy models are
barely used in multi-dimensional HBDs due to the significant
increase of computational complexity. We show that by introducing
an intra-bin point location approximation and an approximate
iterative fuzzification approach, the algorithm can
be simplified and thus SMFSC hardly increases computational
complexity. Experiments on standard shape dataset show
that SMFSC improves upon the Inner Distance Shape Context.
We also applied SMFSC on Content-Based Product Image
Retrieval and the experimental results further validate the
effectiveness of our model.
 We propose a new shape descriptor, Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (MFSC), which is highlighted by its robustness to
deformations. A novel multi-scale fuzzy model is presented
and applied on the widely used shape descriptor Shape Context
to generate MFSC. The multi-scale fuzzy model can handle
shape deformations of different scales, which makes MFSC
robust to various deformations. Experiments on an articulated
shape dataset demonstrate performance improvement
gained by MFSC over existing methods. We also applied
MFSC on a real-world application, Content-Based Product
Image Retrieval, and the experimental results further validate
its effectiveness. We make our code and experimental data
publicly available for future reference.
We propose a new shape descriptor, Multi-scale
Fuzzy Shape Context (MFSC), which is highlighted by its robustness to
deformations. A novel multi-scale fuzzy model is presented
and applied on the widely used shape descriptor Shape Context
to generate MFSC. The multi-scale fuzzy model can handle
shape deformations of different scales, which makes MFSC
robust to various deformations. Experiments on an articulated
shape dataset demonstrate performance improvement
gained by MFSC over existing methods. We also applied
MFSC on a real-world application, Content-Based Product
Image Retrieval, and the experimental results further validate
its effectiveness. We make our code and experimental data
publicly available for future reference.
.png) This paper proposes an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context and low-level visual information. The contextual model estimates the progression of the disease using subject information, such as the time since injury and the knowledge about the location of mTBI. The visual model utilizes texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine to maximize the discrimination in unimodal MR images. These two models are fused to obtain a final estimate of the locations of the mTBI lesion. The models are tested using a novel rodent model of repeated mTBI dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the fusion of both contextual and visual textural features outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches. Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and patients by improving clinical care.
This paper proposes an approach that is able to detect mTBI lesions by combining both the high-level context and low-level visual information. The contextual model estimates the progression of the disease using subject information, such as the time since injury and the knowledge about the location of mTBI. The visual model utilizes texture features in MRI along with a probabilistic support vector machine to maximize the discrimination in unimodal MR images. These two models are fused to obtain a final estimate of the locations of the mTBI lesion. The models are tested using a novel rodent model of repeated mTBI dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the fusion of both contextual and visual textural features outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches. Clinically, our approach has the potential to benefit both clinicians by speeding diagnosis and patients by improving clinical care.
.png) Human gait properties can be affected by various environmental contexts such as walking surface and carrying objects. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for individual recognition by combining different gait classifiers with the knowledge of environmental contexts to improve the recognition performance. Different classifiers are designed to handle different environmental contexts, and context specific features are explored for context characterization. In the recognition procedure, we can determine the probability of environmental contexts in any probe sequence according to its context features, and apply the probabilistic classifier combination strategies for the recognition. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Human gait properties can be affected by various environmental contexts such as walking surface and carrying objects. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for individual recognition by combining different gait classifiers with the knowledge of environmental contexts to improve the recognition performance. Different classifiers are designed to handle different environmental contexts, and context specific features are explored for context characterization. In the recognition procedure, we can determine the probability of environmental contexts in any probe sequence according to its context features, and apply the probabilistic classifier combination strategies for the recognition. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.