
|

|
Ev ve Ofis taşıma sektöründe lider olmak.Teknolojiyi klrd takip ederek bunu müşteri menuniyeti amacı için kullanmak.Sektörde marka olmak.
İstanbul evden eve nakliyat
Misyonumuz sayesinde edindiğimiz müşteri memnuniyeti ve güven ile müşterilerimizin bizi tavsiye etmelerini sağlamak.
Principal Investigator
Bir Bhanu, Center for Research in Intelligent Systems
Room 216, Winston Chung Hall, University of California at Riverside,
Riverside, CA 92521,
Tel. 951-827-3954, Fax. 951-827-2425
bhanu@cris.ucr.edu
http://www.vislab.ucr.edu/PEOPLE/BIR_BHANU/bhanu.php
Co-PIs
Mark Campbell (Cornell University)
Homepage
Chinya Ravishankar (UCR)
Homepage
Amit K Roy Chowdhury (UCR)
Homepage
Postdoctoral
Ninad Thakoor
Federico Pala
Students
Le An, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Anirban Chakraborty, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Zhixin Jin, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Priyanka Khire, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Yingying Zhu, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Xiaojing Chen, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Mithun Chowdhury, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Abir Das, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Lucas de la Garza, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Alex Ivanov, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Rameswar Panda, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Sourya Roy, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Raj Theagarajan, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Zhang Xiu, Graduate Student (research assistant)
Accomplishments
- Major Goals of the Project:
- (a) To develop a synergistic framework and algorithms for a group of fixed and mobile (ground and aerial) sensors to collaborate
on scene understanding in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery scenarios, which are characterized by highly
dynamic and uncertain environments.
- (b) To perform a tight integration of perception and action in a probabilistic framework for truly intelligent robotic systems, and to
advance the field of cyberphysical systems by exploring a new class of synergies across three areas: control, video
understanding and perception, and data management under uncertainty.
- (c) To develop distributed estimation and information planning algorithms to enable a wider range of behaviors in cooperative
robotic teams, which subsequently will enable a better handling of uncertainty, and improved sensing, information collection
and decision making.
- (d) To experimentally validate the framework and algorithms by applying them to the domain of surveillance, using a testbed
incorporating autonomous agents, including mobile and fixed cameras, robots, and unmanned ground or aerial vehicles.
- Accomplishments under these goals:
Major Activities:
- 1) Research in multitarget multisensor tracking and reidentification, and online adaptation of the learned models.
2) Research into managing and querying data under conditions of uncertainty. In particular, since a great deal of data
of current interest is spatiotemporal, rather than just spatial, we have been investigating the management and querying
of spatiotemporal data.
- Specific Objectives:
- 1) Develop methods for tracking multiple targets in a network of sensors by considering the physical constraints from the scene geometry.
2) Develop methods for online adaptation of the learned models as more data is available.
3) Managing and querying data under uncertainty.
4) Informationbased planner with guarantees and joint exploration and tracking.
5) Multiperson tracking by online learned grouping and group structure preserving pedestrian tracking.
- Significant Results:
-
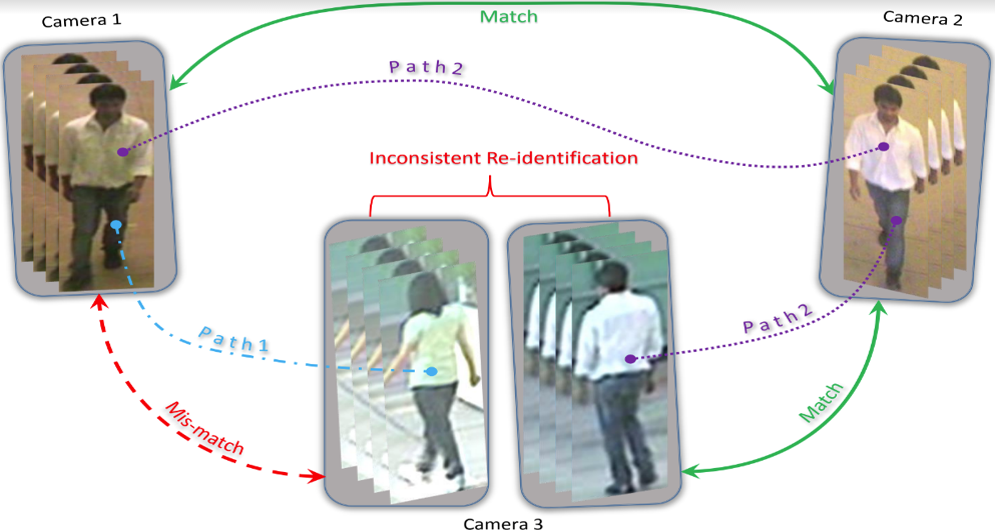
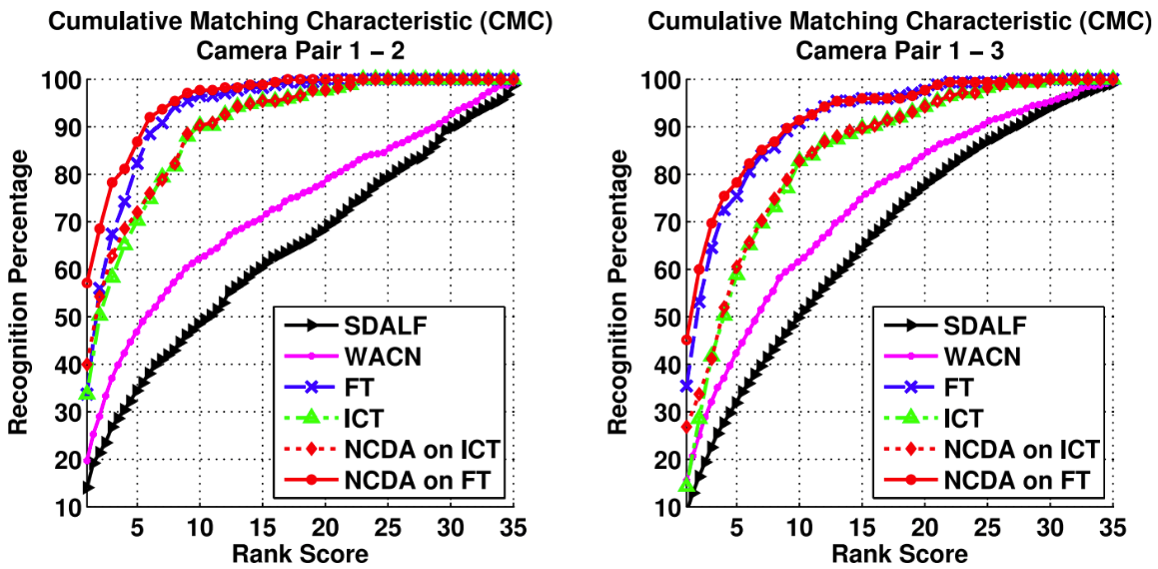
A) Multitarget Tracking and Data Association in a Sensor Network Considering Scene
Constratins: Existing data association techniques mostly focus on matching pairs of
datapoint sets and then repeating this process along spacetime to achieve long term
correspondences. However, in many problems such as person reidentification, a set of
datapoints may be observed at multiple spatiotemporal locations and/or by multiple
agents in a network and simply combining the local pairwise association results between
sets of datapoints often leads to inconsistencies over the global spacetime horizons. In
this work, we propose a novel Network Consistent Data Association (NCDA) framework
formulated as an optimization problem that not only maintains consistency in association
results across the network, but also improves the pairwise data association accuracies.
The proposed NCDA can be solved as a binary integer program leading to a globally
optimal solution and is capable of handling the challenging dataassociation scenario
where the number of datapoints varies across different sets of instances in the network.
We have also achieved an online implementation of NCDA method that can dynamically
associate new observations to already observed datapoints in an iterative fashion, while
maintaining network consistency. (Lead: Roy Chowdhury)
- Address consistent matching as a data-association task over network perspective
- Formulate an optimization problem to maximize overall pairwise similarity while abiding by network level constraints
-
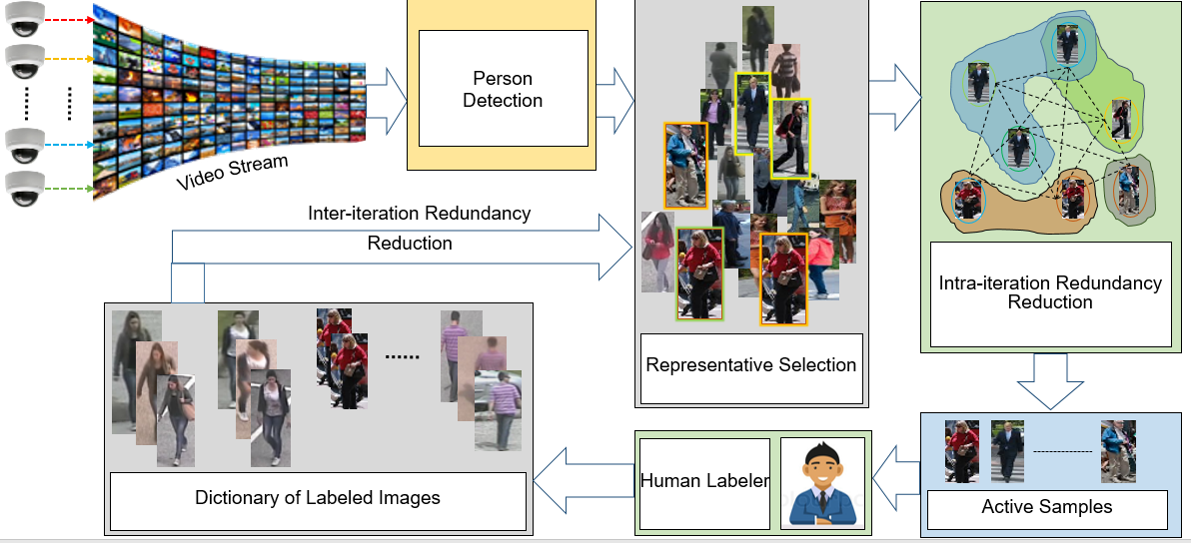
B) Online Adaptation of Learned Models in Sensor Networks: Most traditional multicamera
person reidentification systems rely on learning a static model on tediously labeled
training data. Such a framework may not be suitable for situations when new data arrives
continuously or all the data is not available for labeling beforehand. Inspired by the ‘value
of information’ active learning framework, we propose a continuous learning person reidentification
system with a human in the loop. The human in the loop not only provides
labels to the incoming images but also improves the learned model by providing most
appropriate attribute based explanations. These attribute based explanations are used to
learn attribute predictors along the way. The overall effect of such a strategy is that
starting with a few annotated images, the system begins to improve via a symbiotic
relationship between the man and the machine. The machine assists the human to
speed the annotation and the human assists the machine to update itself with more
annotation so that more and more distinct persons are reidentified as more and more
images come in. (Lead: Roy Chowdhury)
- Propose a sparse representative selection based approach
- Formulate as a convex optimization problem, which endorses selection of samples with the most variabilities
-
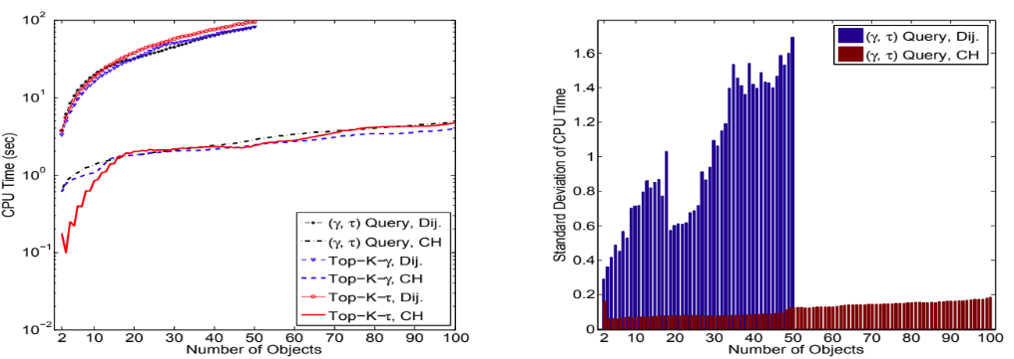
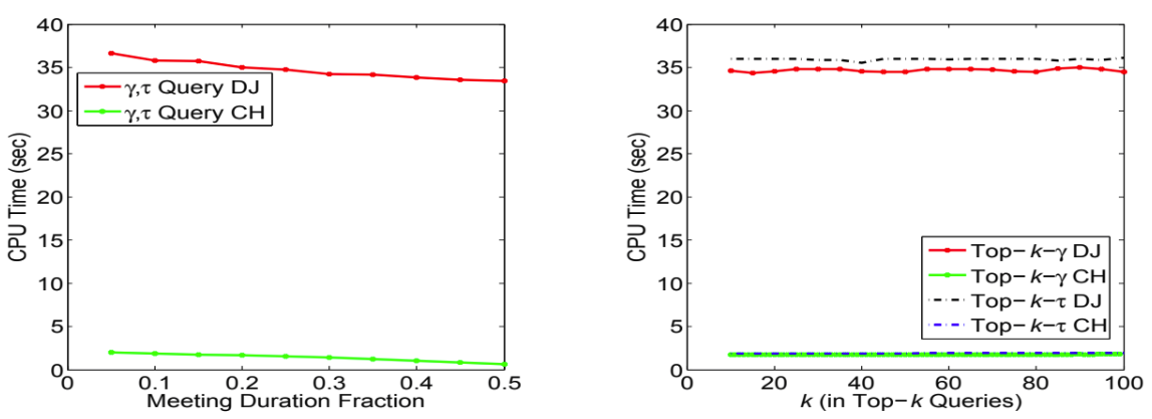
C) Managing and Querying Data Under Uncertainty: When objects travel so that their
positions cannot be monitored continuously, and there are “blind” regions and periods, we
have developed efficient techniques to determine whether groups of moving objects may
have assembled within these blind regions. Our techniques are based on the widelyused
approach of Contraction Hierarchies, and have proved to be very efficient. (Lead:
Ravishankar)
- Introduce the novel and important class of assembly queries:
- “Assembly discovery”: determine whether two or more moving objects could have had a meeting within a region of interest
- “Assembly planning”: arrange for meetings for a group of friends visiting a city without violating their remaining schedules
- Provide efficient solutions given incomplete trajectory information, using the topology of the underlying transportation network
- Present a formal model for the general problem and prove the correctness of our algorithm
- Utilize a preprocessing method based on Contraction Hierarchies to gain orders of magnitude speed up over the naïve Dijkstra-based methods
-
D) Information based Planner with Guarantees: Developed an optimal path planner which
maximizes information collection, but with a probabilistic constraint of not getting lost.
Formal proofs are defined, and empirical evaluations are conducted. A receding horizon
approach to real time work is developed using a novel tail cost approximation. The work
is verified with an indoor robot over multiple trials. (Lead: Campbell)
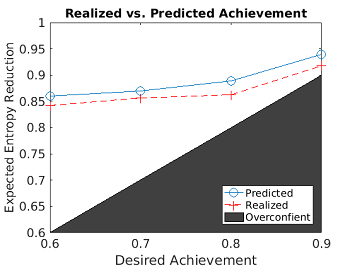 Key results:
Key results:
- General info gathering framework
- Maximizing information goals
- Probabilistic guarantees
- Asymptotic guarantees as the # of samples increases
- Bound on the reward for partially known environments
- Speeds computation (>1000x) to real time
- Validation by simulation/experiment
-
E) Joint exploration and tracking: Developed a formal solution to the multirobot multiobject
exploration and tracking problems simultaneously. A hierarchical architecture is
used to coordinate robotic agents in the tracking of multiple ObjectsofInterest (OIs)
while simultaneously allowing the task to remain computationally efficient. The primary
contributions of this work are probabilistic guarantees on tracking performance,
automatic discovery of new OIs, a seamless transition from exploration to tracking, and
the automatic balancing of exploration and tracking. (Lead: Campbell)
-
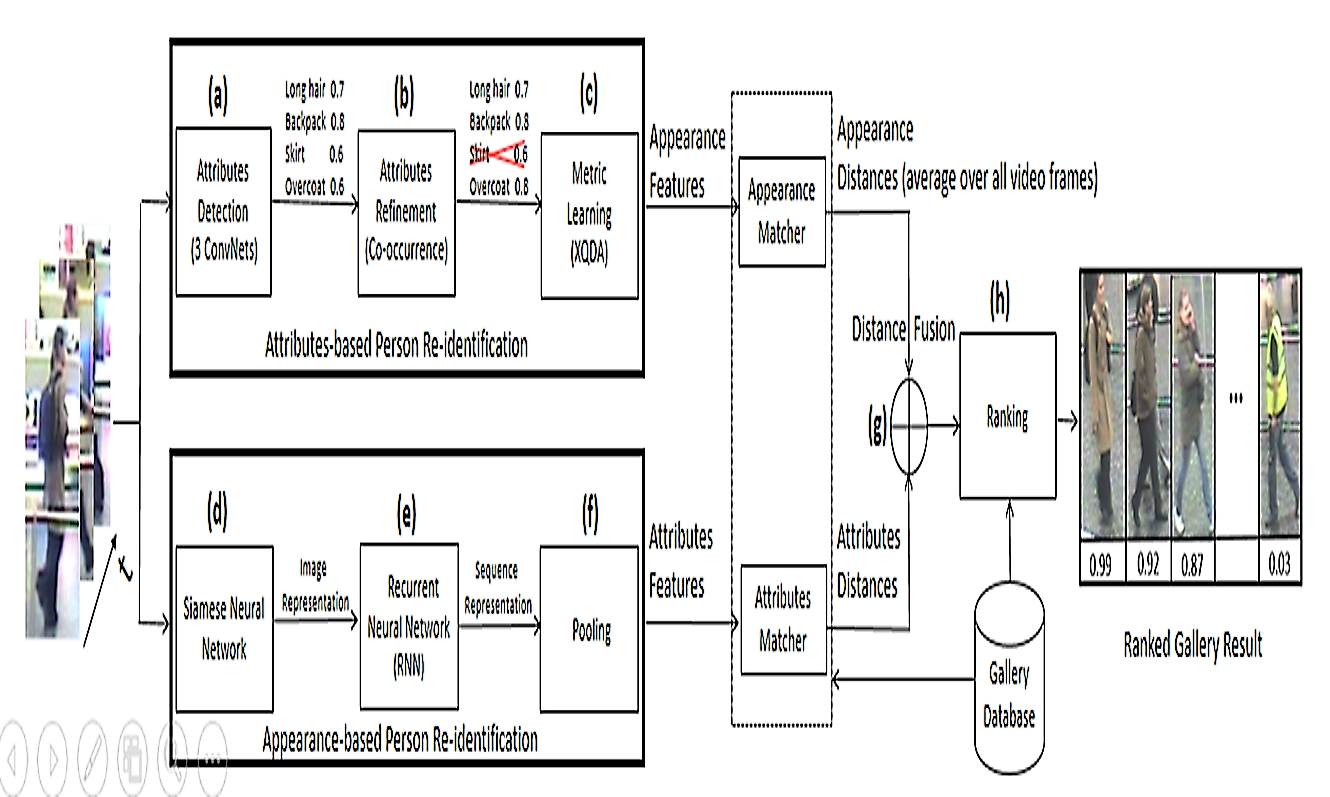
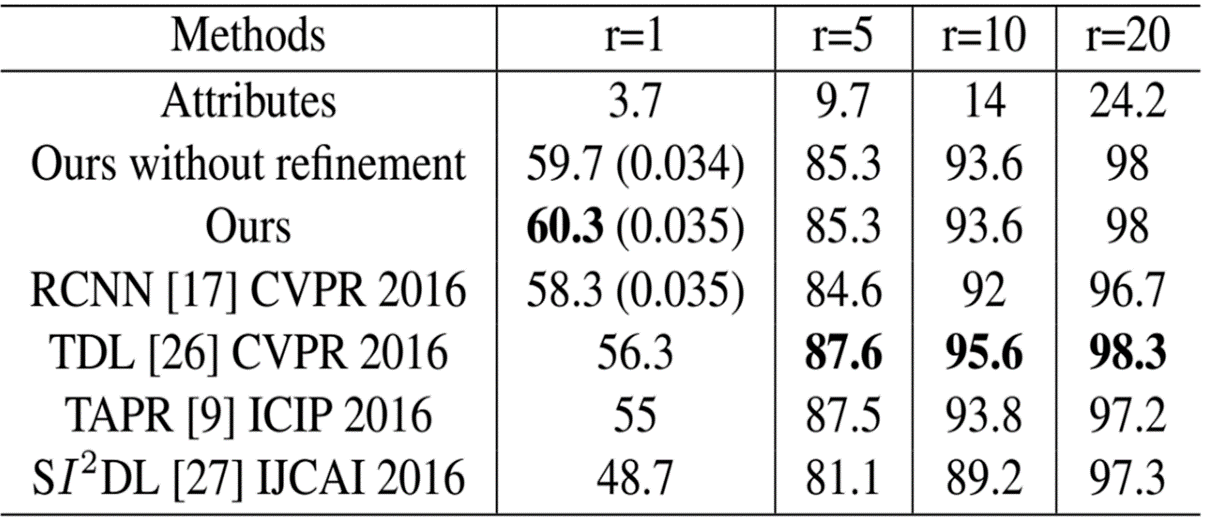
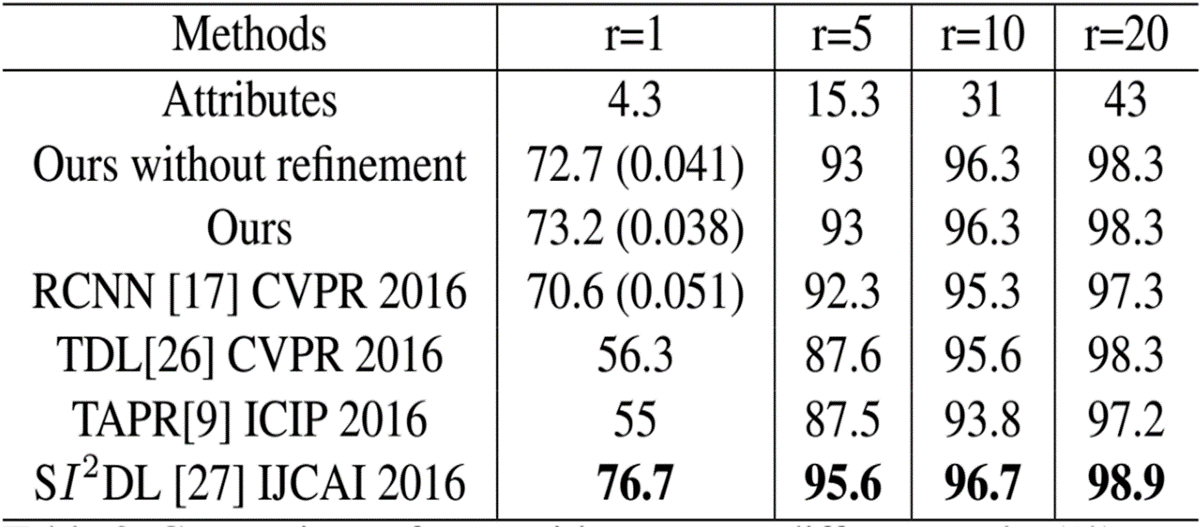
F) Attributes Cooccurrence Pattern Mining: Person reidentification has received
considerable attention in the image processing, computer vision and pattern recognition
communities because of its huge potential for videobased surveillance applications and
the challenges it presents due to illumination, pose and viewpoint changes among nonoverlapping
cameras. Being different from the widely used lowlevel descriptors, visual
attributes (e.g., hair and shirt color) offer a human understandable way to recognize
people. We have developed a new way to take advantage of them. First, convolutional
neural networks are adopted to detect the attributes. Second, the dependencies among
attributes are obtained by mining association rules, and they are used to refine the
attributes classification results. Third, metric learning technique is used to transfer the
attribute learning task to person reidentification. Finally, the approach is integrated into
an appearancebased method for videobased person reidentification. Experimental
results on two benchmark datasets indicate that attributes can provide improvements
both in accuracy and generalization capabilities. (Lead: Bhanu)
- Visual attributes (e.g., hair and shirt color) offer a human understandable way to recognize people
- Design three ConvNets for attributes detection
- Exploit co-occurrence information to improve attributes’ descriptive capabilities
- Propose an attributes-based method and then combine it with an appearance-based model for final prediction
- Achieve better and more consistent results on two public datasets
-
G) Multiperson Tracking by Online Learned Grouping: An online approach to learn
elementary groups containing only two targets, i.e., pedestrians, for inferring high level
context is introduced to improve multiperson tracking. In most existing data associationbased
tracking approaches, only lowlevel information (e.g., time, appearance, and
motion) is used to build the affinity model, and each target is considered as an
independent agent. Unlike those previous methods, an online learned social grouping
behavior model is used to provide more robust tracklet affinities. A disjoint grouping
graph is used to encode social grouping behavior of pairwise targets, where each node
represents an elementary group of two targets, and two nodes are connected if they
share a common target. Probabilities of the uncertain target in two connected nodes
being the same person are inferred from each edge of the grouping graph. Relationships
between elementary groups are discovered by group tracking, and a nonlinear motion
map is used for explaining nonlinear motion pattern between elementary groups. The
proposed method is efficient, able to handle group split and merge, and can be easily
integrated into any basic affinity model. The approach is evaluated on four data sets, and
it shows significant improvements compared with stateoftheart methods. (Lead: Bhanu)
-
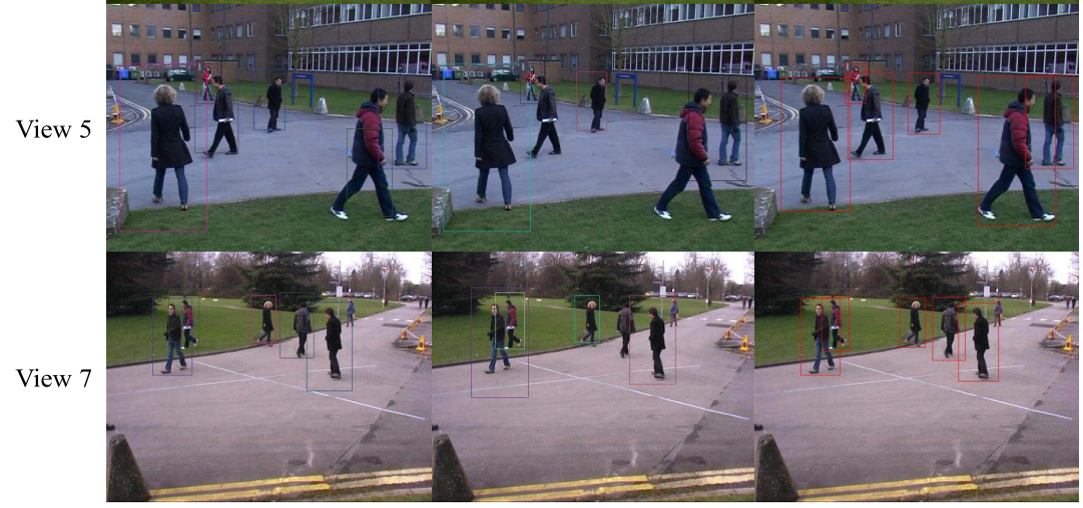
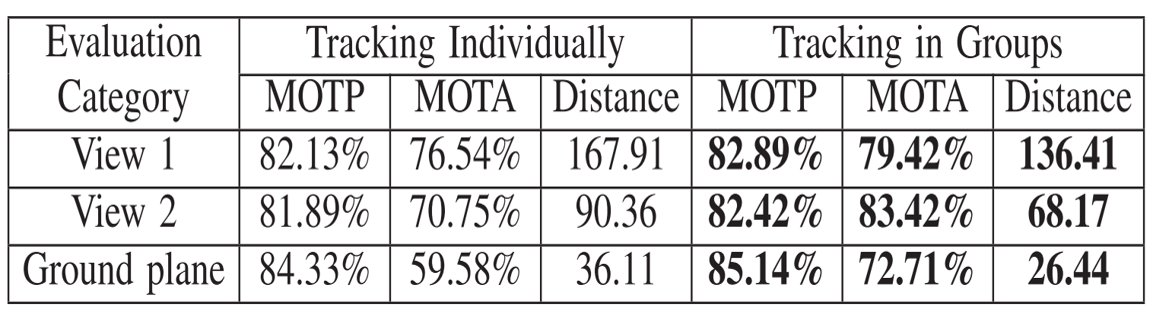
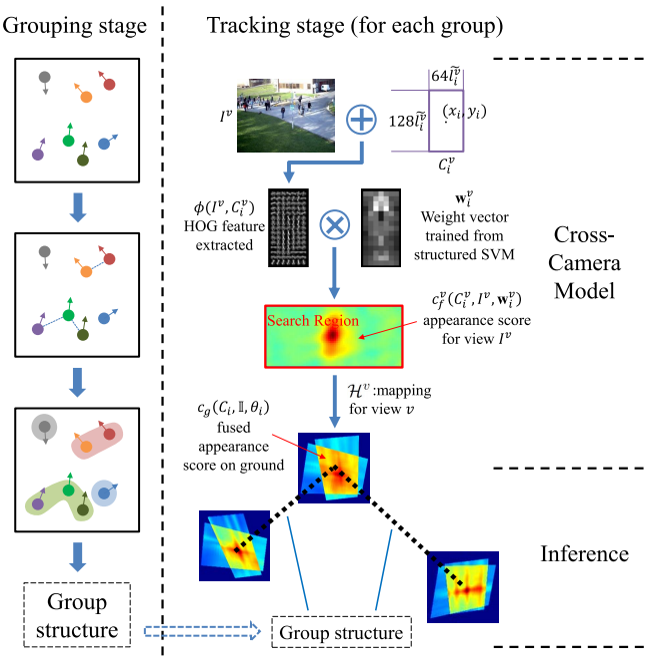
H) Group Structure Preserving Pedestrian Tracking: In order to improve tracking
performance, many ideas have been proposed, among which the use of geometric
information is one of the most popular directions in recent research. We proposed a
novel multicamera pedestrian tracking framework, which incorporates the structural
information of pedestrian groups in the crowd. In this framework, first, a new crosscamera
model is proposed, which enables the fusion of the confidence information from
all camera views. Second, the group structures on the ground plane provide extra
constraints between pedestrians. Third, the structured support vector machine is adopted
to update the crosscamera model for each pedestrian according to the most recent
tracked location. The experiments and detailed analysis are conducted on challenging
data. The results demonstrate that the improvement in tracking performance is
significant when a group structure is integrated. (Lead: Bhanu)
- A new cross-camera model is proposed, which enables the fusion of the confidence information from all camera views
- Group structures on the ground plane provide extra constraints between pedestrians
- The structured support vector machine is adopted to update model
- Excellent results are obtained on challenging data

- Key Outcomes or other Achievements:
- Publications in major conferences and journals. In many cases the software has been
released along with the papers. Three Special Issues of Journals have been published
(IEEE Computer, IEEE Sensor and Computer Vision and Image Understanding).
Overview articles have also been published in IEEE publications.
- New dataset for multicamera person tracking and reidentification.
- New dataset for object recognition in unconstrained environments
- Algorithms and software for lidar/vision data fusion for tracking people from moving
robots, and an information optimal exploration planner.
- What opportunities for training and professional development has the project provided?
- More than six graduate students have been partially supported by this grant. Four of the students have completed their PhDs and two more are PhD candidates.
- At Cornell university three graduate students have been partially supported by this grant, with one who finished an MS and the other two are still in the program.
- How have the results been disseminated to communities of interest?
- Publications, software and datasets. For example, a paper describing results on handling uncertainty will appear in the 25th
ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. One of the authors on this
paper was an employee of ESRI, the leading provider of software systems for managing spatial and geographic data.
- What do you plan to do during the next reporting period to accomplish the goals?
- We will focus on online learning approaches for adaptation of scene understanding models in unconstrained environments.
- Refinement of attributebased learning methods with uncertainty associated with objects.
- Study the distributed version of the information exploration planner.
- Exploitation of parallelism for the improvement of query processing.
Journals or Juried Conference Papers
- A. Das, R. Panda, A. RoyChowdhury (2015). Active Image Pair Selection for Continuous Person Reidentification. IEEE Intl. Conf. on Image Processing. Link
- Ivanov, A., & Campbell, M. (2018). Joint Exploration and Tracking: JET. IEEE Control Systems Letters. 1 (2), 43. Link
- Ivanov, A., & Campbell, M. (2018). Uncertainty Constrained Robotic Exploration: An Integrated Exploration Planner. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology. Link
- N. Thakoor and B. Bhanu (2016). Selective Experience Replay in Reinforcement Learning for Reidentification. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Link
- R. Panda, A. Bhuiyan, V. Murino, A. RoyChowdhury (2017). Unsupervised Adaptation of Reidentification Models in Dynamic Camera Networks. In Preparation. Link
- R. Panda, A. Das, A. RoyChowdhury (2016). Video Summarization in a MultiView Camera Network. International Conf. on Pattern Recognition. Link
- R. Theagarajan, F. Pala and B. Bhanu (2017). EDeN: Ensemble of Deep Networks for Vehicle Classification. Traffic Surveillance Workshop and Challenge (TSWC2017) held in conjunction with IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Link
- Reaz Uddin, Vassilis Tsotras, Chinya Ravishankar. Indexing of Approximate Spatiotemporal Trajectories Using Hilbert Curves. Under Review.
- S. Yang, L. An, Y. Lei, M. Li, N. Thakoor, B. Bhanu and Y. Liu (2017). A Dense Flowbased Framework for Realtime Object Registration Under Compound Motion. Pattern Recognition. 63 279. Link
- X. Chen, Z. Qin, L. An and B. Bhanu (2016). Multiperson tracking by online learned grouping model with nonlinear motion context. IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology. 26 (12), 2226. Link
- X. Zhang, F. Pala and B. Bhanu (2017). Attributes Cooccurrence Pattern Mining for Videobased Person Reidentification. IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signalbased Surveillance. Link
- Z. Jin, L. An and B. Bhanu (2017). Group Structure Preserving Pedestrian Tracking in Multicamera Video Network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video technology. 27 (10), 2165. Link
Other Conference Papers and Presentations
- Reaz Uddin, Michael Rice, Chinya Ravishankar, and Vassilis Tsotras (2017). Assembly Queries: Planning and Discovering Assemblies of Moving Objects Using Partial Information. Proc. 25th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. Redondo Beach, CA. Link
Software
- Various Softwares Under Development.
Websites
Acknowledgement
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Project ID No. CNS-1330110. Any opinions,
findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
|
|







 Key results:
Key results:





